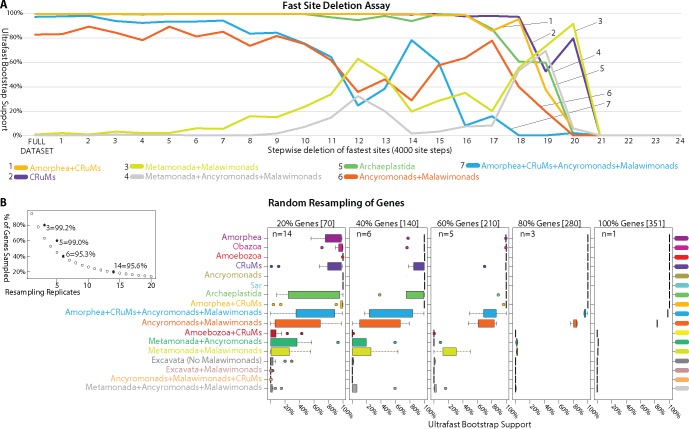
Fig. 2.
—Effects of fast evolving sites and random subsampling of genes on our phylogenomic analyses. (A) Sites were sorted based on their rates of evolution estimated under the LG + F+Γ model and removed from the data set from highest to lowest rate. Each step has 4,000 of the fastest evolving sites removed progressively. The bootstrap values (UFBOOT; LG + C60 + F+Γ-PSMF model) for each bipartition of interest are plotted. (B and C) Effects of random subsampling of genes within the 351-gene data set. The following bipartitions were examined but received nearly 100% support across the fast site deletion series (data not shown); Amorphea, Obazoa, Amoebozoa, Ancryomonads, and Sar. The following bipartitions were examined but received nearly 0% support across the fast site deletion series (data not shown); Amoebozoa + CRuMs, Metamonada + Ancyromonads, Excavata (No Malawimonads), Excavata + Malawimonads, and Ancyromonads + Malawimonads + CRuMs. (B) Effects of random subsampling of genes on the bipartitions of interest. Inset panel is the calculation of the number of replicates (n) necessary for a 95% probability of sampling every gene when subsampling 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80% of genes using the formula: 0.95 = 1−(1−x/100)n, where x is the percentage of genes subsampled. UFBOOT support values for all nodes of interest with the variability of support values illustrated by box-and-whisker plots.