Figure 1.
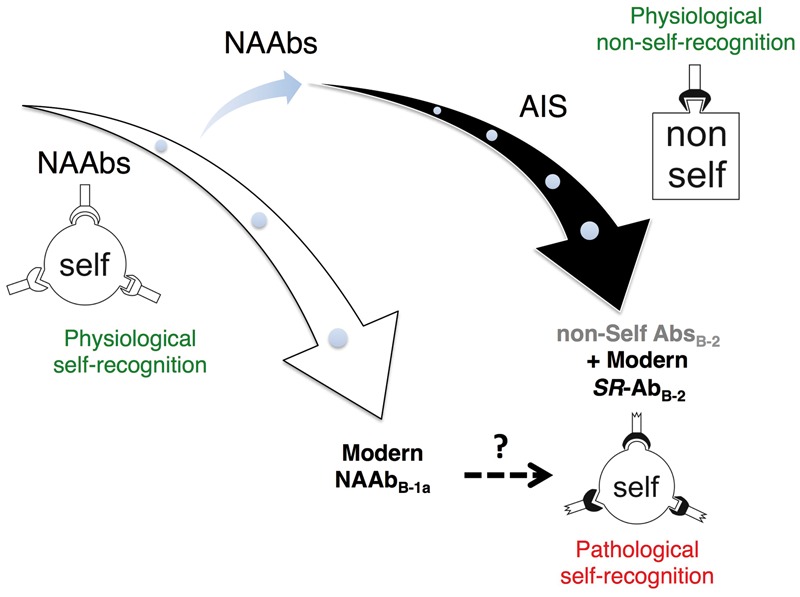
Hypothesis for the origin of the AIS in jawed vertebrates. Subsequent to the whole genome duplication that predated the radiation of jawed vertebrates (blue arrow), the AIS—a non-self-recognition system—gradually emerged from a regulated self-recognition system that is presently part of the IIS and produces natural autoantibodies via B-1a cells (NAAbB-1a). A population-genetic environment wherein the power of random genetic drift exceeds the power of selection might have favored the emergence of the AIS. NAAbB-1a are physiologically produced; they contribute to tissue homeostasis and protect from pathological self-reactivity. SR-AbB-2 are the AIS’s counterpart of NAAbB-1a. They can cause pathological self-reactivity and are normally counter-selected during the production of B-2 cell-derived non-self-targeting Abs (non-Self AbsB-2). It still remains unclear whether pathological self-reacting Abs result from misregulated B-1a cells, B-2 cells or subgroups thereof. Furthermore, the primary source of pathological self-reacting Abs may vary depending upon the types of AD
