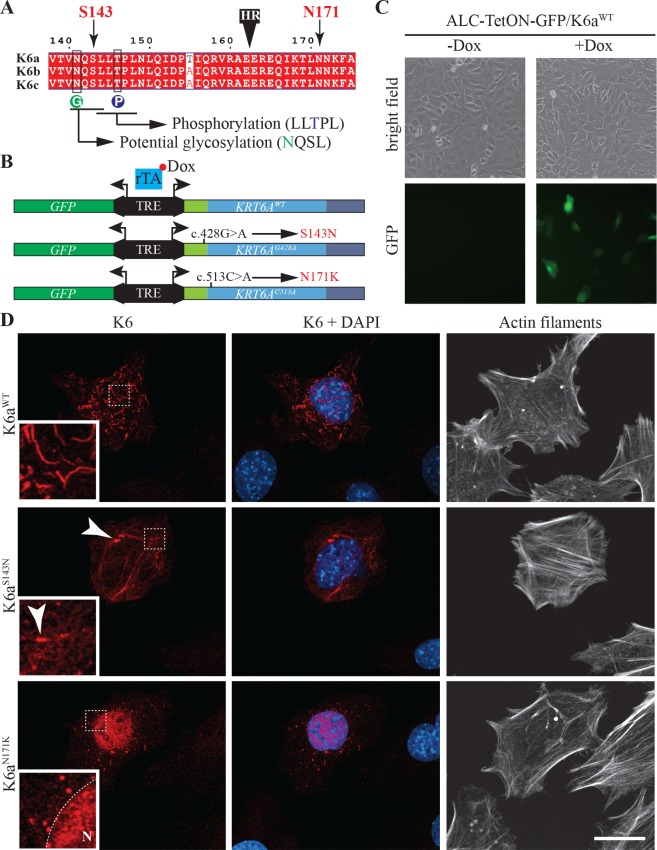
Fig 4. Effects of S143N and N171K mutations on the assembly of K6a in ameloblast-like cells.
(A) Alignment of K6a, K6b and K6c protein sequences between amino acids 138 and 175 showing the position of serine 143 and asparagine 171 on both sides of the transition between the head and the rod domain (black box labeled HR). Serine 143 is right upstream of an LLS/TPL consensus phosphorylation site (blue circle labeled P) that is highly conserved in type II keratins. Serine 143 is also part of an NQSL potential N-glycosylation site (green circle labeled G). (B) Schematic representation of pBi4-GFP/K6a bidirectional constructs used for tetracycline inducible expression of GFP with KRT6AWT, KRT6AG428A (produces K6aS143N) or KRT6AC513A (produces K6aN171K mutant). When transfected into cells expressing the transactivator rTA, transgene expression through binding of rTA to the tetracycline responsive element (TRE) can be induced by addition of doxycycline (Dox) to the culture medium. (C) Detection of GFP induction in ameloblasts-like cells stably expressing rTA (ALC-TetON) transfected with pBi4-GFP/K6a constructs and grown with or without Dox. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of K6a subcellular distribution (red) in ALC-TetON cells producing K6aWT, K6aS143N or K6aN171K. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) and actin filaments are stained with phalloidin conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647 (white).