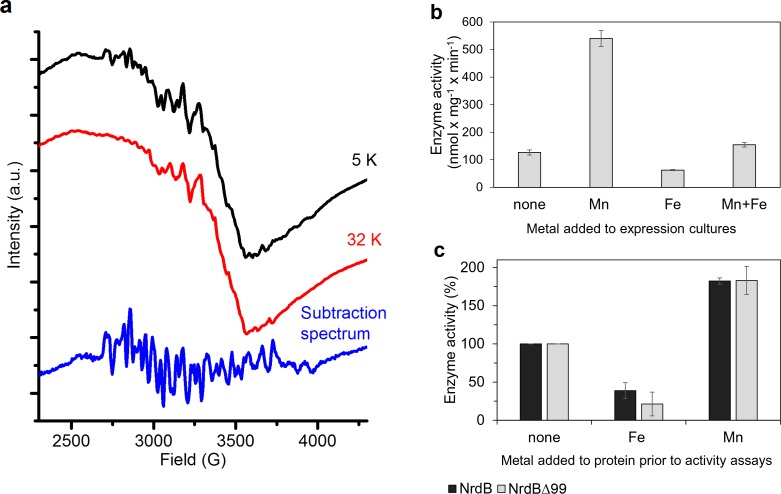
Figure 7. Type of dinuclear metal center of L. blandensis NrdB and metal-dependency of enzyme activity.
(a) X-band EPR spectra of catalytically active, non-reconstituted, samples recorded at 5 K (black, top); 32 K (red, middle) (signal intensity multiplied by 3.7 for clarity; multiline spectrum obtained by subtraction of a scaled 32K spectrum from the 5K spectrum (blue, bottom) (signal intensity multiplied by three for clarity). Instrument settings: microwave frequency = 9.28 GHz; power = 1 mW; modulation amplitude = 10G; modulation frequency = 100 kHz. (b) Enzyme activity of NrdB∆99 purified from heterologously expressed cultures grown with addition of different divalent metal ions as indicated; the Mn-sample was used for the EPR analysis. (c) Enzyme activity was measured after addition of a total concentration of 20 µM divalent metal ions to 10 µM of wild-type or NrdB∆99 protein as indicated. Enzyme activity without addition of metals was set as 100% and corresponded to 592 and 217 nmol mg−1 min−1 for wild type and NrdB∆99 enzymes respectively. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of three measurements.
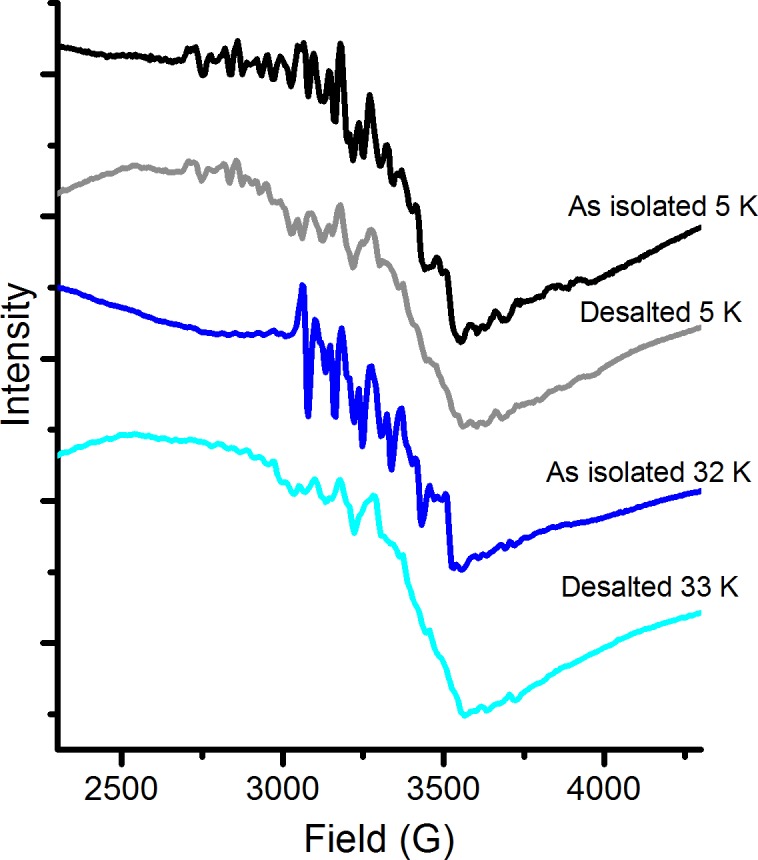
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. X-band EPR spectra recorded at 5 K and 32 K of catalytically active samples before and after desalting treatment.