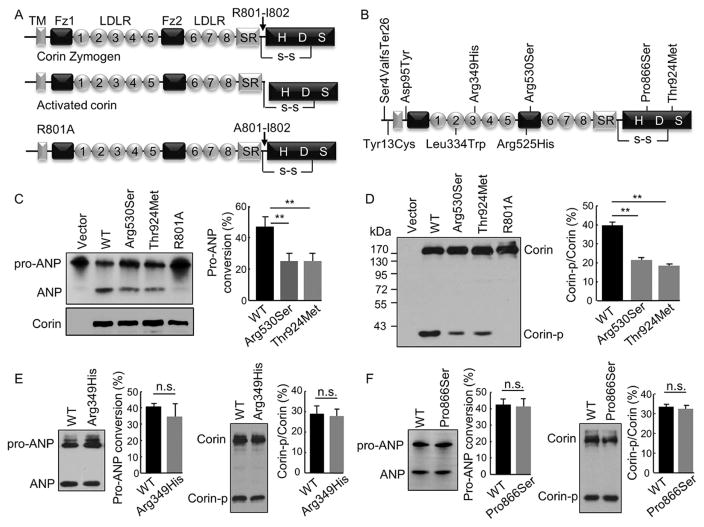
FIGURE 1.
Pro-ANP processing activity and zymogen activation of corin variants. (A) Domain structures of corin zymogen, activated corin, and the activation cleavage site mutant R801A. TM: transmembrane; Fz: frizzled; LDLR: LDL receptor-like; SR: scavenger receptor-like; H, D and S in the protease domain are active sites His, Asp, and Ser, respectively. (B) Locations of identified variants. (C) Pro-ANP processing activity of p.Arg530Ser and p.Thr924Met analyzed by Western blotting (left). Pro-ANP to ANP conversion was quantified (right). Data were from nine independent experiments; **P < 0.001 versus WT. (D) Corin expression and zymogen activation in transfected HEK293 cells analyzed by Western blotting under reducing conditions (left). Ratio of the cleaved corin protease domain fragment (Corin-p) versus corin zymogen fragment (Corin) was quantified (right). Data were from nine independent experiments; **P < 0.001 versus WT. Pro-ANP processing activity (left) and zymogen activation (right) of p.Arg349His (E) and p.Pro866Ser (F) were analyzed by Western blotting. Data were from three to five independent experiments; n.s.: not significant with P values > 0.05 versus WT