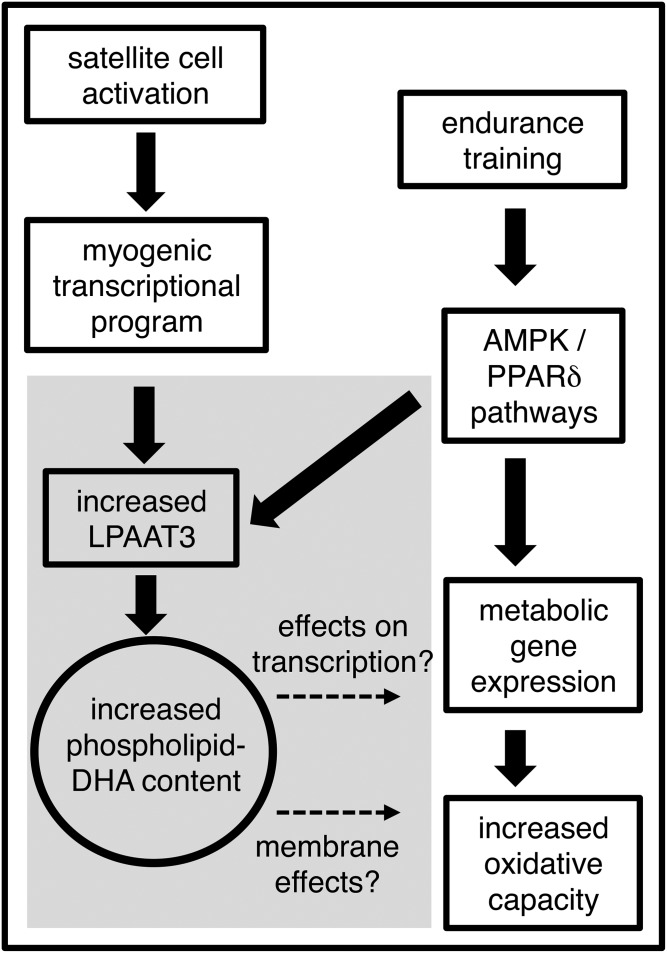
Fig. 7.
Proposed mechanism and function of enhanced DHA content in endurance-trained skeletal muscle. LPAAT3 levels may increase in activated satellite cells as part of the myogenic transcriptional program. Exercise-activated AMPK and PPARδ pathways, which stimulate metabolic gene expression, may also enhance LPAAT3 levels in myofibers. DHA incorporation into membranes may alter their biophysical properties and thereby affect cellular metabolism. DHA incorporation into membranes may also impact free DHA levels to influence activities of lipid-sensing transcription factors such as PPARs. Findings from this study are in the shaded region; dashed arrows indicate possible metabolic effects of the enhanced phospholipid-DHA content.