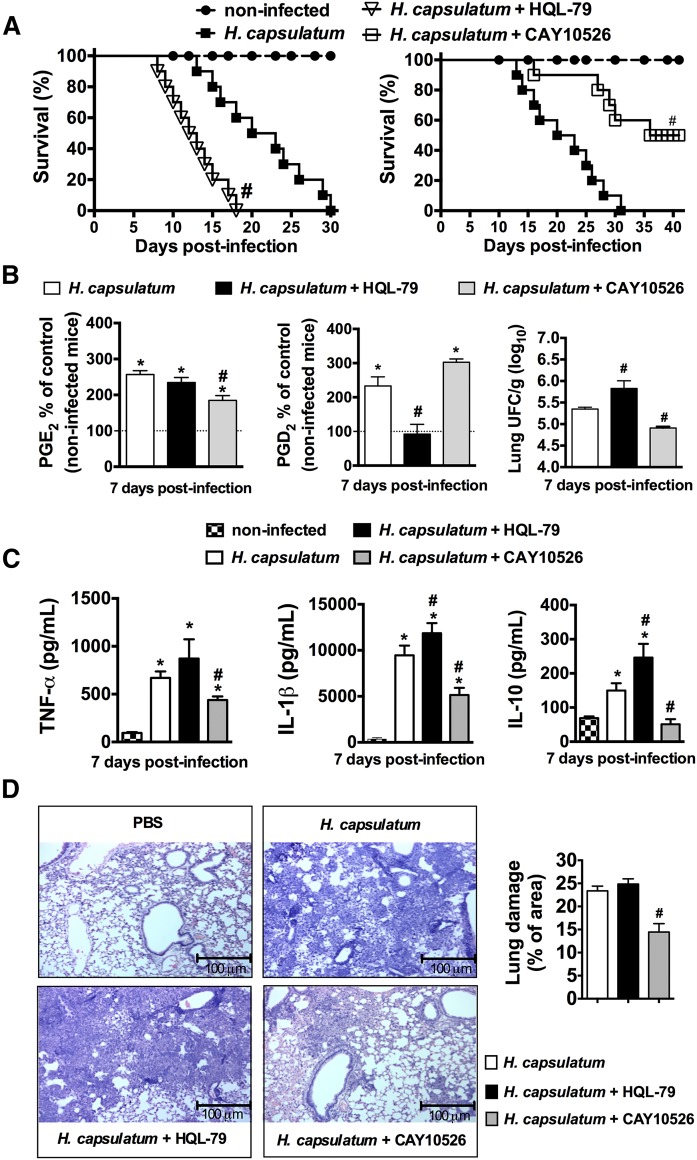
Fig. 7.
PG synthesis inhibition differently affects the survival of mice infected with lethal inoculum of H. capsulatum and inflammatory parameters. A: Mice were treated daily orally with water or HQL-79 (inhibitor of PGD2 synthesis: 3 mg/kg/0.5 ml) for 30 days (n = 10) or treated daily with CAY10526 (inhibitor of PGE2 synthesis: 5 mg/kg/0.5 ml) for 40 days (n = 10). A group of noninfected mice was used as controls (n = 10). B: Lipid mediators PGD2 and PGE2 in the lung parenchyma were measured by enzyme immunoassay and fungal burden in the lungs. C: Lung cytokine concentrations (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-10) were determined at 7 days following infection by ELISA. D: Lung tissues were also processed and stained with H&E to detect leukocyte infiltration after 7 days. Percent of cell infiltrated area corresponding to extent of lung damage. # P < 0.05 (H. capsulatum + H2O vs. H. capsulatum + HQL-79 or H. capsulatum + CAY10526 treatment); * P < 0.05 [PBS (non-infected mice, dashed line) vs. H. capsulatum + H2O or H. capsulatum + HQL-79 or H. capsulatum + CAY10526 treatment]. A: Log rank test for survival analysis was used. B–D: One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test were used. Data are representative of two independent experiments (±SEM).