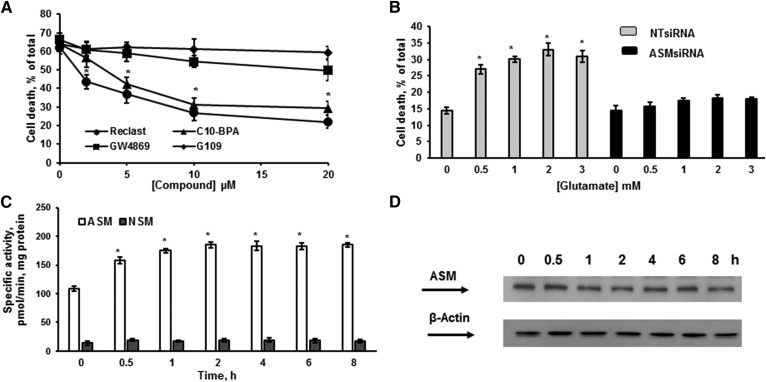
Fig. 5.
ASM activation is critical for OL survival after glutamate treatment. A: OLs were treated with 1 mM glutamate with/without ASM (Reclast and C10-BPA) and NSM (GW4869 and epoxyquinone G109) inhibitors and relative cell survival was determined. Data are mean ± SE, *P < 0.05, n = 12. B: OLs were transfected with 20 nM of nontargeting siRNA pool (NT siRNA) or 20 nM of specific siRNA pool targeting different regions of the ASM gene (ASMsiRNA). Cells were plated and cultured for 24 h, then treated with 1 mM glutamate and relative cell survival was measured 24 h following glutamate treatment. Data are mean ± SE, *P < 0.05, n = 12. C. Time-course of specific ASM and NSM activity changes was determined following OL treatment with 1 mM glutamate. The enzyme activity is expressed as picomoles of C15-SM per minute per milligram protein. Data are mean ± SE, *P < 0.05, n = 12. D: The time-course of ASM protein expression changes was assessed following OL exposure to 1 mM glutamate. Cell lysates (30 μg/lane) were analyzed using anti-ASM antibody. To confirm equal loading of samples, the membranes were stripped and probed with anti-β-actin (Sigma-Aldrich) antibody. Data are representative of three independent experiments.