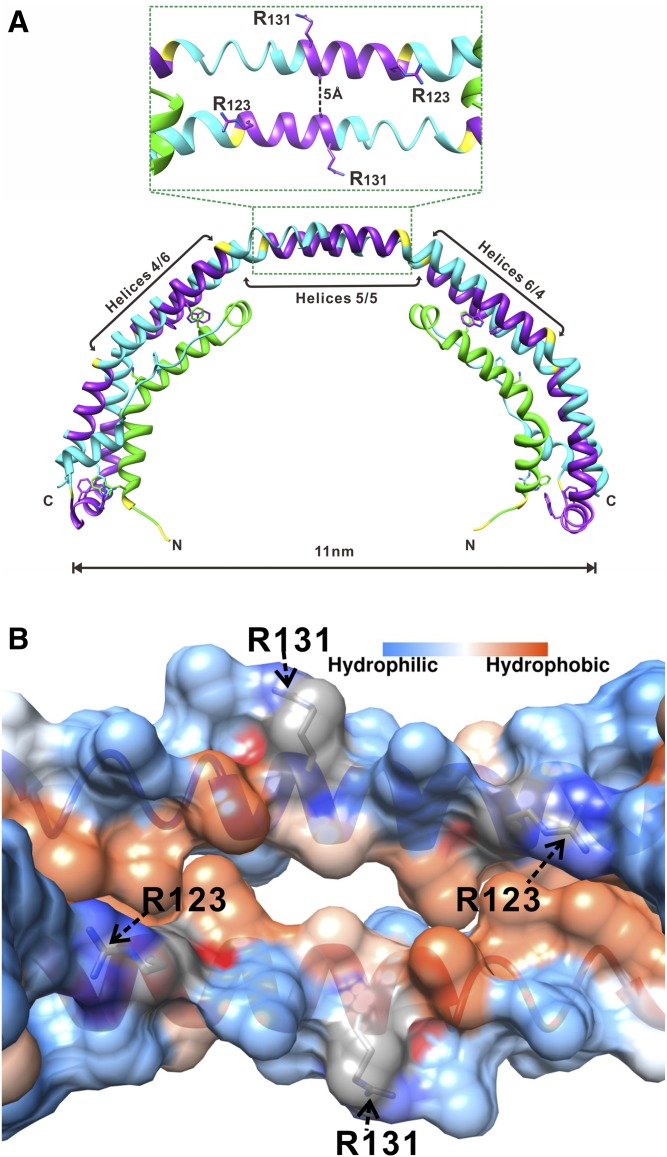
Fig. 1.
Location of Arg123 and Arg131 in the structure of apoA-I. A: X-ray crystal structure of Δ(185−243)apoA-I (Protein Data Bank entry 3R2P) showing a crystallographic dimer with the central opening (amphipathic tunnel), ∼5 Å in diameter, between the antiparallel helices 5/5 (29). B: Inside view of the amphipathic central tunnel formed by the central antiparallel helices 5/5 with the surface colored according to the residue hydrophobicity or charge. The central tunnel has a strongly charged outside surface and a hydrophobic inside surface. The two positively charged Arg123 residues, one from each apoA-I antiparallel molecule, are projecting toward the hydrophobic region at each end of the tunnel. Two Arg131 residues, one from each antiparallel molecule, are located on the outside surface of the tunnel.