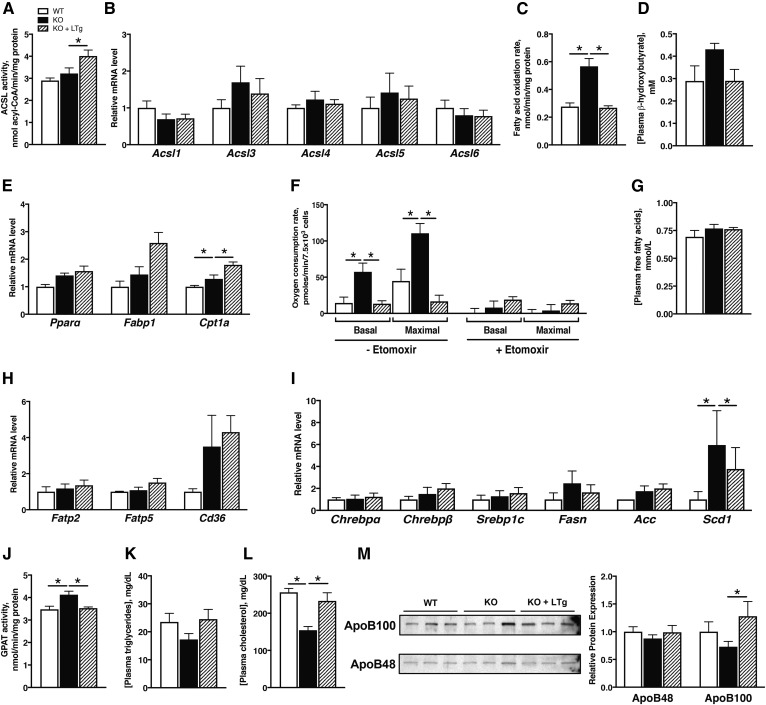
Fig. 5.
Them1 expression suppresses fatty-acid oxidation in livers of high-fat-fed mice. Mice were fed a high-fat diet for 14 weeks and sacrificed at age 18 weeks. Analyses included ACSL activity (A) (n = 3–6 per group), relative mRNA expression of Acsl isoforms (B) (n = 4 per group), rates of fatty acid oxidation (C) (n = 3–5 per group), plasma concentrations of β-hydroxybutryate (D) (n = 6 per group), and relative mRNA expression of Pparα and its target genes (E) (n = 4 per group). F: Basal and maximal OCR values were measured in primary cultures hepatocytes isolated from 12-week-old mice (representative of n = 2 independent experiments, 6–8 replicates per experiment) following exposure to 300 µM palmitate, with or without being treated with the CPT1 inhibitor, etomoxir. Additional analyses using the high-fat-fed mice were plasma concentrations of FFAs (G) (n = 6 per group); mRNA expression of fatty acid transporter (H) and lipogenic transcription factors and target genes (I) (n = 6 per group); as well as GPAT activities (J) (n = 4 per group) and plasma concentrations of TGs (K) and cholesterol (L) (n = 6 per group). M: Immunoblot analysis of apoB48 and apoB100 expression in the plasma (n = 3 per group). * P < 0.05.