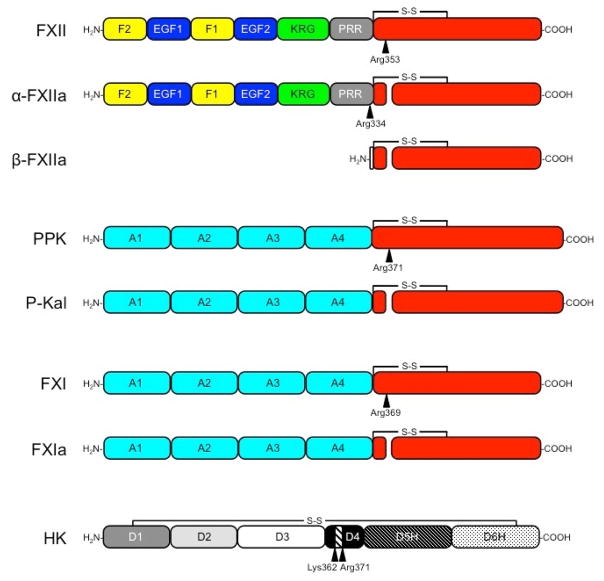
Figure 1. The Contact Factors.
Schematic diagrams showing domains in each contact factor. Sites of proteolysis during activation are indicated by arrows. The residues immediately N-terminal to each cleavage site are indicated. Trypsin-like protease domains are indicated in red. FXII is an 80 kDa polypeptide that is cleavage after Arg353 to form αFXIIa. Cleavage of αFXIIa after Arg334 separates the non-catalytic and catalytic domains, forming βFXIIa. The FXII non-catalytic domains are the fibronectin type 2 (F2), epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibronectin type 1 (F1), and kringle (K) domains, and a proline–rich region (PRR). PPK is a 93 kDa polypeptide that is cleaved after Arg371 to form α-kallikrein (P-Kal). FXI is a homodimer of 80 kDa polypeptides. Each subunit of the dimer is converted to FXIa by cleavage after Arg369. The non-catalytic portions of PPK and FXI contain four apple domains (A1 to A4). HK is comprised of 6 domains (D1–D4, D5H and D6H). The nanopeptide sequence for bradykinin (Arg363-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg371) is in D4. D5 facilitates binding to surfaces and D6 contains overlapping binding sites for FXI and PPK.