Figure 6.
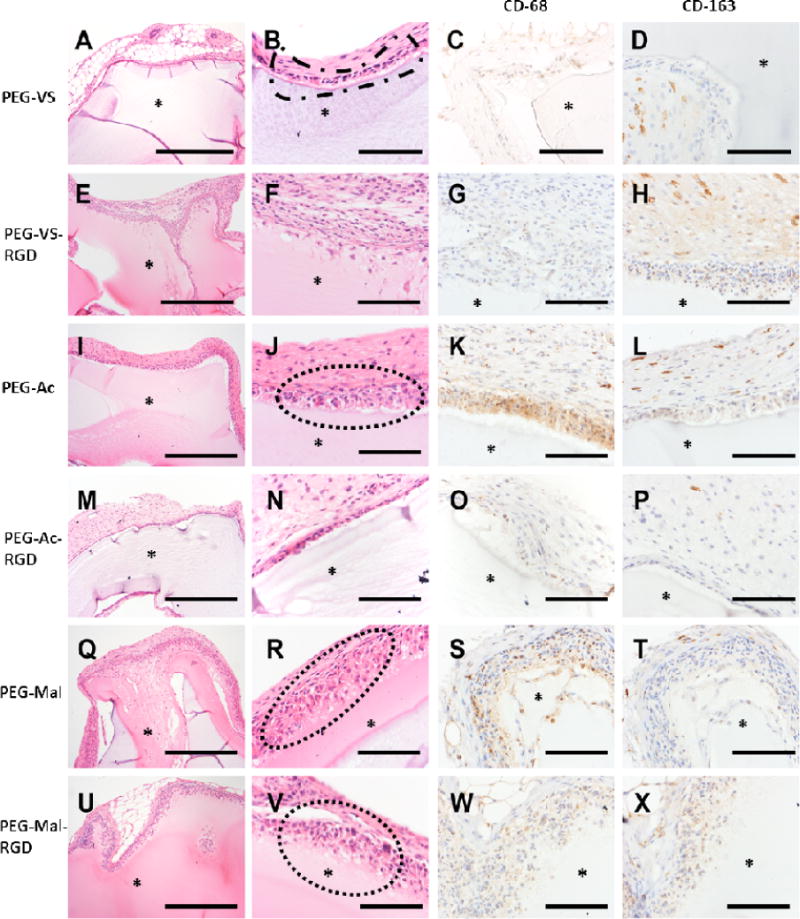
Histological images of 8-arm PEG types after implantation for 28 days. (A, B) PEG-VS, (E, F) PEG-VS-RGD, (I, J) PEG-Ac, (M, N) PEG-Ac-RGD, (Q, R) PEG-Mal and (U, V) PEG-Mal-RGD. Host response to implanted PEG types as observed: (B) PEG-VS implant with retraction artifact and loosely adherent capsule composed of attenuated epithelioid cells (dashed outline). (J) PEG-Ac implant with multilayered cellular capsule overlying granulation tissue with prominent angiogenesis and frequent multinucleate giant cells (dashed outline). (R, V) PEG-Mal implant with infiltration into and partial resorption of the hydrogel matrix (dotted outline). (C, G) Presence of macrophage M1 (CD-68 staining) were observed in (G, K) PEG-Ac and (S, W) PEG-Mal hydrogels. Whereas macrophage M2 (CD-163 staining) observed in weak to strong presence between PEG hydrogel types (P, T, X, D, H and L). (*) PEG hydrogel. Magnification 10× (A, E, I, M, Q, U) scale bar, 500 μm. Magnification 40× (B, C, D, F, G, H, J, K, L, N, O, P, R, S, T, V, W, X), scale bar, 50 μm.
