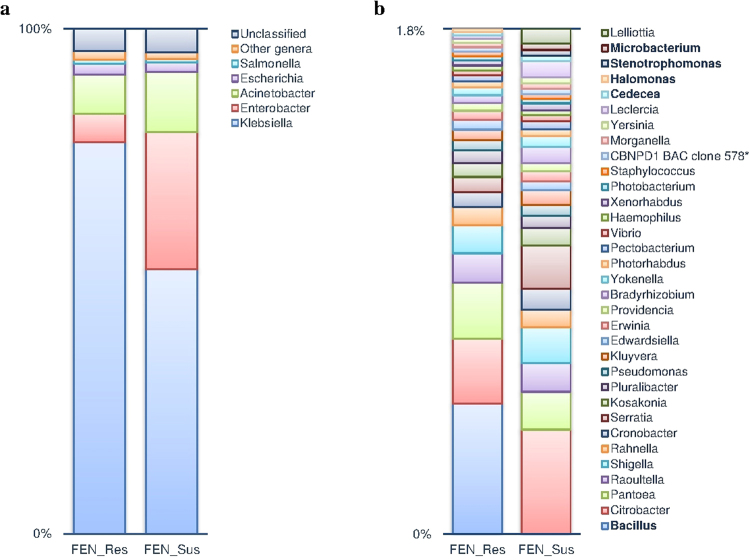
Figure 1.
Differential bacterial composition between fenitrothion resistant and susceptible An. albimanus. Based on the alignment of sequencing reads (FEN_Res, n = 83,947,332; FEN_Sus, n = 60,444,900) to the NCBI-NR protein database, 37 bacterial genera and one uncultured β-proteobacterium* were identified in fenitrothion resistant and susceptible An. albimanus samples. Five genera; Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Acinetobacter, Escherichia and Salmonella comprised over 93% of identified genera in both samples and are considered as the predominant genera in this study. Plot (a) shows the proportions of each predominant genera as well as the proportions of unclassified reads in fenitrothion resistant and susceptible samples. Thirty two bacterial genera comprising the remaining proportion (1.8%) of the microbiota are grouped as ‘other genera’ and expanded in plot (b). Bacterial genera that are unique to either resistant or susceptible An. albimanus are presented in bold typeface. There were differential abundances of predominant (a) and other (b) genera between FEN_Res and FEN_Sus, with significant (p < 0.001) enrichment of Klebsiella in FEN_Res.