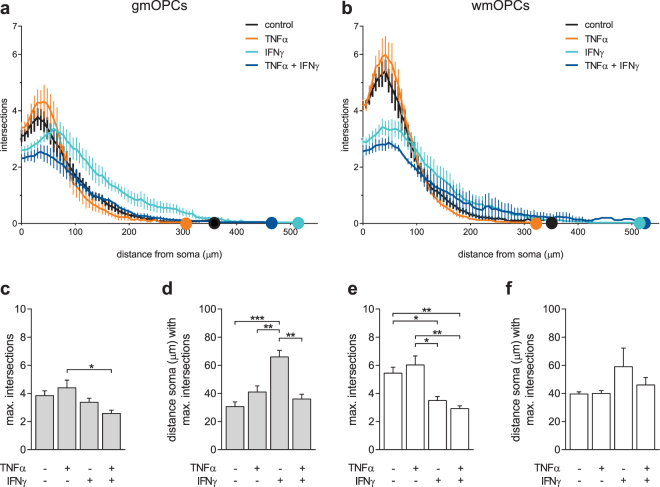
Figure 6.
IFNγ decreases the maximum number of intersections in gmOPCs and wmOPCs and increases the distance of the soma with the maximum number of intersections of gmOPCs. Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) isolated from the cortex (gmOPCs) and non-cortex (wmOPCs) of neonatal rat forebrains were left untreated or treated with 10 ng/ml TNFα, 500 U/ml IFNγ, or a combination of TNFα and IFNγ for 48 hours in the presence of PDGF-AA and FGF-2. OPCs were stained for the OPC cell surface marker A2B5 to visualize their morphology (see Fig. 4e). The number of processes that intersect with the concentric circles of Sholl analysis as a function of the distance from the soma (a,b), maximum intersections (c,e) and distance of the soma with the maximum number of branch points (d,f) are shown. Grey bars represent gmOPCs (a,c,d), white bars represent wmOPCs (b,e,f). Error bars show the standard error of the mean. Note that the maximum number of intersections is decreased in wmOPCs upon treatment with IFNγ, and in both gmOPCs and wmOPCs upon treatment with IFNγ combined with TNFα, while the distance of the soma with the maximum number of intersections is increased upon IFNγ treatment in gmOPCs. Statistical analyses were performed using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s post-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) to test for differences between treatments and their respective control. Scale bar is 50 µm.