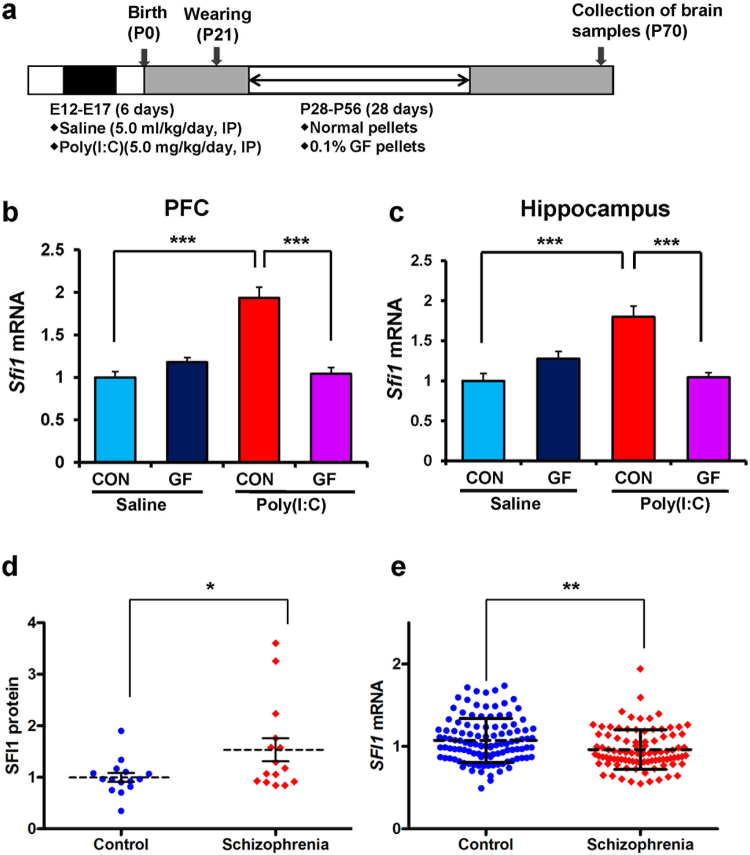
Figure 5.
Expression of Sfi1 mRNA in the PFC and hippocampus from the adult offspring after prenatal poly(I:C) exposure and expression of SFI1 protein and SFI1 mRNA in schizophrenia. (a) Schedule of treatment and behavioral tests. Saline (5 ml/kg/day) or poly(I:C) (5.0 mg/kg/day from E12 to E17) was injected into pregnant mice. Normal food pellets or 0.1% GF food pellets were given to juvenile offspring from D28 to D56. Subsequently, normal food pellets were given to all mice for 14 days (D57-). Brain samples were collected at D70. (b): Sfi1 mRNA in the PFC: There was significant effects (poly(I:C): F1,22 = 25.39, P < 0.001; GF: F1,22 = 20.28, P < 0.001; interaction: F1,22 = 45.97, P < 0.001). (c) Sfi1 mRNA in the hippocampus: There was significant effects (poly(I:C): F1,22 = 9.29, P = 0.006; GF: F1,22 = 6.65, P = 0.017; interaction: F1,22 = 31.01, P < 0.001). The value is expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5–7). ***P < 0.001 compared to poly(I:C) + control group. (d) Expression of SFI1 protein in the parietal cortex from patients (n = 15) with schizophrenia was significantly (P = 0.034) higher than that of controls (n = 15). The value is expressed as the mean ± S.D. *P < 0.05 compared to control group. (e) Expression of SFI1 mRNA in the hair-follicle from patients (n = 94) with schizophrenia was significantly (P = 0.002) lower than that of controls (n = 117). The value is expressed as the mean ± S.D. **P < 0.01 compared to control group.