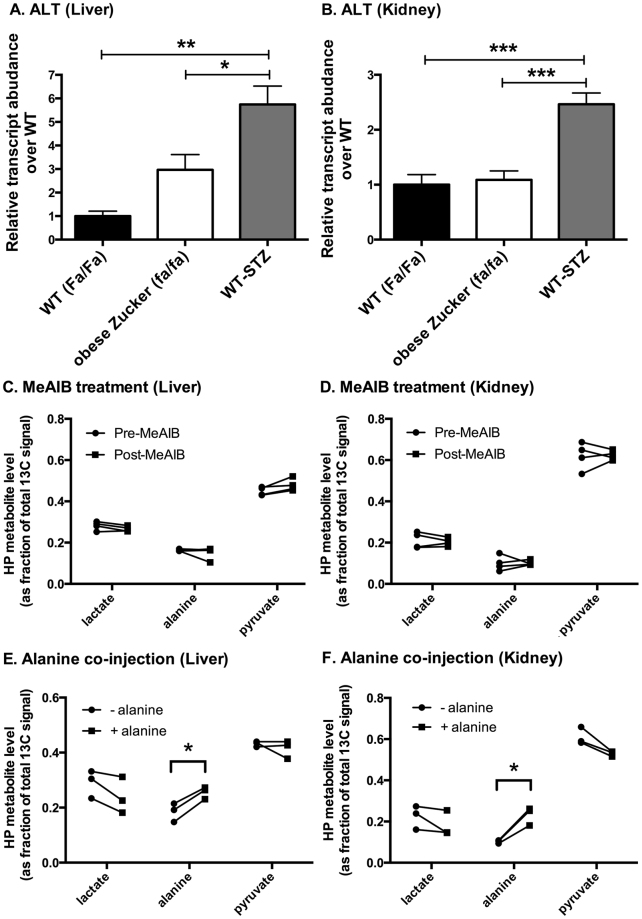
Figure 3.
Investigation of factors that could influence the HP alanine signal level. Panels A&B: rtPCR measurements of ALT expression in liver (A) and kidney (B) tissues of age and sex matched WT (Fa/Fa) (n = 4), obese Zucker (fa/fa), (n = 9) and WT-STZ (n = 6) rats. Panels C&D: Effect of amino acid transport system A inhibition (1000 mg/kg i.v. MeAIB treatment, 90 minutes prior to “post-MeAIB” data point) on metabolites of HP [1-13C]pyruvate in liver (C) and kidney (D) of normal fed Sprague Dawley rats (n = 4). Panels E&F: Effect of co-injection with HP [1-13C]pyruvate of equimolar unlabeled alanine, on HP metabolite signals detected in liver (E) and kidney (F) of normal fed Sprague Dawley rats (n = 3). For PCR, the fold changes were measured relative to WT (Fa/Fa) and calculated with 2−ΔCt method. The data were normalized to β-actin. All PCR data represent mean+/−S.E.M. from three independent experiments, and statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction for multiple comparisons. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) For C–E, individual metabolites were compared using paired, two-tailed t-tests. (*p < 0.05).