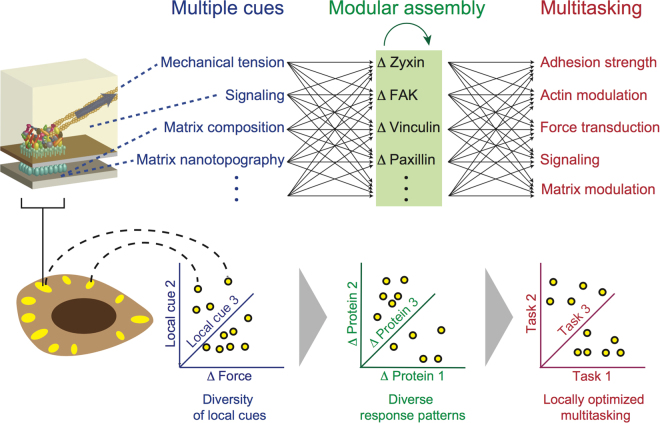
Figure 7.
A model for the molecular diversity in the mechano-responsiveness of focal adhesions and its coupling with their modular mode of assembly and multitasking. The molecular diversity in the responses of focal adhesions to actomyosin perturbations is attributable to multiple factors, including their pre-perturbation internal state, the local change in force level, past changes in force levels, local signaling within the cell and local matrix properties. Hence, assimilation and encoding of these spatially varying cues by each focal adhesion cause distinct patterns of molecular changes in different focal adhesions. The modular mode of focal adhesions assembly enables the shaping of the response patterns, as it allows changing the stoichiometric ratio between the components within a focal adhesion. In turn, the flexibility in setting the response patterns can enable a focal adhesion to adjust the proportions between its multifunctional components, so that collectively they perform correctly its multiple tasks given its local cues.