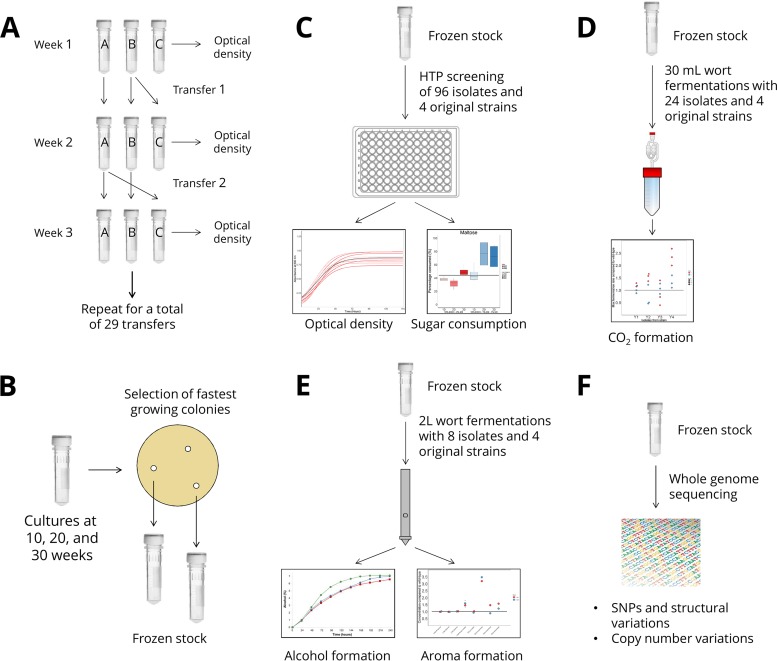
FIG 1.
Experimental overview. (A) Thirty consecutive batch fermentations were carried out with four different yeast strains and two different ethanol-containing media in duplicate adaptation lines. (B) An initial set of isolates were obtained by selecting fast-growing colonies on solidified versions of the adaptation media. (C) High-throughput (HTP) screening of all the isolates was performed in a malt extract-based screening medium containing ethanol. The best-performing isolates were chosen for further screening based on maltose and maltotriose consumption. (D) Small-scale wort fermentations were performed with selected isolates to ensure they were able to ferment wort efficiently and perform in media without exogenous ethanol. (E) Two-liter-scale wort fermentations replicating industrial conditions were performed with 8 variant strains (Table 1), and vital aroma compounds of the resulting beers were analyzed. (F) The genomes of the 8 variant strains were sequenced and compared to those of the wild-type strains. For more information, see Materials and Methods.