Fig. 2.
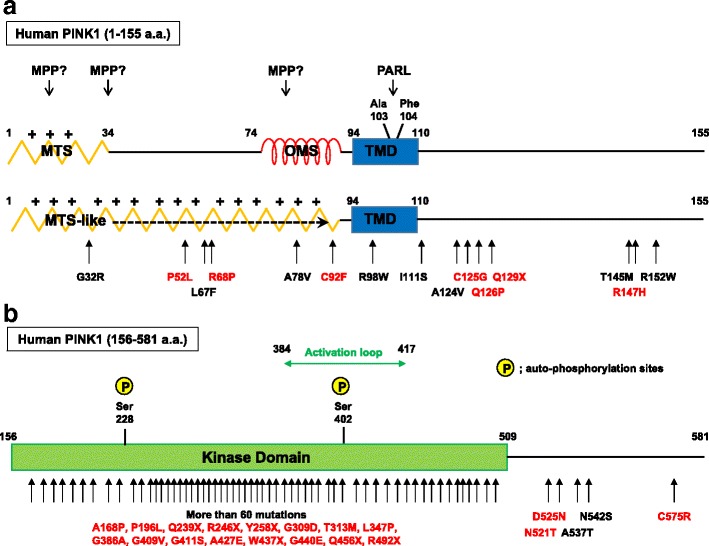
The domain structure of human PINK1. a The N-terminus of PINK1 (amino acids 1–155) contains three important domains for the determination of sub-mitochondrial localization; the mitochondria targeting sequence (MTS), the transmembrane domain (TMD), and the newly identified outer mitochondrial membrane localization signal (OMS) (upper panel). However, MTS could be longer (lower panel), and the precise cleavage sites of MPP have not been determined. PARL cleaves between Ala103 and Phe104 within TMD. b PINK1 has a kinase domain in its C-terminus (amino acids 156–581). Ser228 and Ser402 are auto-phosphorylation sites of PINK1. Arrows indicate PD-associated mutations. Mutations in red have been experimentally verified as loss of function mutations [86]. Most of the mutations reside in the kinase domain
