Table 1.
List of immune dysfunctions caused by sustained type I interferon (IFN-I) signaling which are reversibly rescued by the interferon-α/β receptor (IFNR) blockade.
| Phenotype Improvement(s) | Model | Virus(es) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased cytokine producing virus-specific CD4/CD8 (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2); improved antiviral responses | 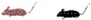 |
HIV, LCMV | [12,13,23,26,34] |
| Reduced expression of PD-1, TIM-3, TIGIT, BATF, CD160 on CD8 (decreased cell exhaustion) |  |
HIV | [12,34] |
| Reduced KI67+ population in CD4/CD8; decrease of HIV-mediated T-cell hyperactivation |  |
HIV | [12] |
| Reduced HLA-DR, CD38, CD69, CD80 expression in CD4/CD8; decrease of HIV-mediated T-cell hyperactivation |  |
HIV | [12,34,41*,53*] |
| Decrease of caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in total and specific CD4 T-cells | 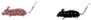 |
HIV, LCMV | [13,54,55*] |
| Accelerating neutralizing Abs production |  |
LCMV | [18] |
| Reduced PD-L1 and IL-10 expression in DCs, mono and macro. Decreased IL-10 levels in plasma/sera |  |
HIV, LCMV | [23,26,41*] |
| Reduced IL-1 and IL-18 levels, and inflammasome activation in DCs and monos; decreased CD80 expression in monos |  |
HIV, LCMV | [23,26,41*] |
| Increase of splenocyte cell numbers (DCs, macrophages, CD4, CD8, B and matural killers) |  |
LCMV | [23,26,52] |
| Proper splenic architecture organization |  |
LCMV | [23,26] |
| Decreased CXCR4 expression on GC B Increased levels of specific Ab production and specific ASCs |  |
LCMV | [52] |
| Decreased caspase-3+ apoptotic virus-specific GC B (by counteracting plasmablast differentiation); B expansion |  |
LCMV | [54] |
| Increased virus-specific B number; Decreased CTL CD8-mediated kill of specific B |  |
LCMV | [56] |
| Reduced TRAIL/DR5-mediated apoptosis in CD4 |  |
HIV | [55*] |
| Decreased % of TRAIL+ and apoptotic CD4 |  |
HIV | [57] |
| Increased Fas-mediated apoptosis in CD4 and CD8 T-cells |  |
HIV | [58*] |
| Increased expression of BTLA on CD4 T-cells; reduced hyper-immune activation |  |
HIV | [59*] |
| Increased Th1 differentiation in late primed virus-specific CD4 |  |
LCMV | [60] |
 : Humans;
: Humans;  : Humanized mice;
: Humanized mice;  ; Mice; *: in vitro viral infection; ASC: antibody-secreting cells; CD: cluster of Differentiation; TNF: tumor Necrosis Factor; IL: interleukin; PD: programmed Death Protein; TIM: T-cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin; TIGIT: T-cell Ig and ITIM domain; BATF: basic leucine zipper transcription factor ATF-like; LCMV: Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; KI: proliferation Marker, Ki-67 is a prototype monoclonal Ab and was first produced in Kiel, Germany; HLA-DR: human leukocyte antigen - antigen D related; DCs: dendritic cells; CXCR: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor; GC: germinal center; ASCs: antibody secreting cells; CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocytes; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand; Th1: Type I T helper cells; BTLA: B and T lymphocyte attenuator.
; Mice; *: in vitro viral infection; ASC: antibody-secreting cells; CD: cluster of Differentiation; TNF: tumor Necrosis Factor; IL: interleukin; PD: programmed Death Protein; TIM: T-cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin; TIGIT: T-cell Ig and ITIM domain; BATF: basic leucine zipper transcription factor ATF-like; LCMV: Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; KI: proliferation Marker, Ki-67 is a prototype monoclonal Ab and was first produced in Kiel, Germany; HLA-DR: human leukocyte antigen - antigen D related; DCs: dendritic cells; CXCR: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor; GC: germinal center; ASCs: antibody secreting cells; CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocytes; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand; Th1: Type I T helper cells; BTLA: B and T lymphocyte attenuator.
