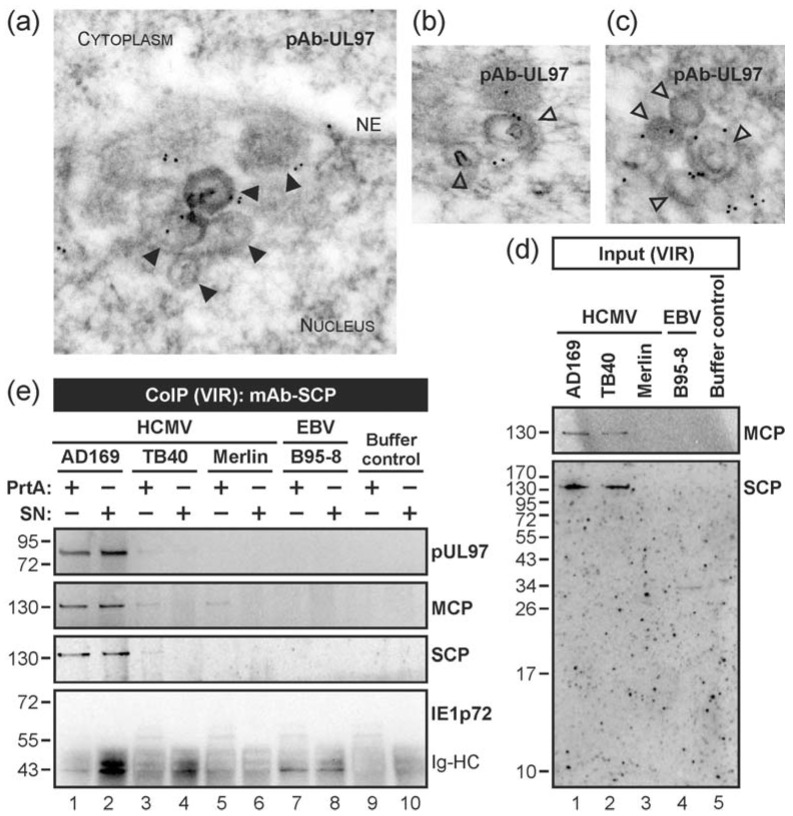
Figure 3.
Association of the HCMV-encoded protein kinase pUL97 with viral capsids in the nucleus. (a–c) HCMV-infected HFFs were harvested at 3 dpi and subjected to immunogold staining of viral pUL97. Samples were analysed by TEM, 35,970-fold magnification. NE, nuclear envelope; open arrowheads, intranuclear HCMV capsids; filled arrowheads, HCMV capsids budding at nuclear membranes; (d,e) CoIP analysis with cell-free virions (VIR) as input. Virions from HCMV strains AD169, TB40 or Merlin (harvested from identical quantities of HFF producer cell layers, i.e., one T175 flask each) were lysed followed by CoIP using protein A-purified mAb-SCP (PrtA) or unpurified supernatant of mAb-SCP hybridoma cultures (SN). EBV strain B95-8 or buffer served as CoIP negative controls ((d) lanes 4–5; (e) lanes 7–10). CoIP samples (e) and expression control samples (input; (d)) were both subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against the indicated proteins. Note, no band was detected at the molecular weight of approximately 72 kDa using an antibody directed against immediate early protein 1 (IE1p72; (e), lower panel) pointing to the specificity of the CoIP. Ig-HC, cross-reactive band for immunoglobulin heavy chain.