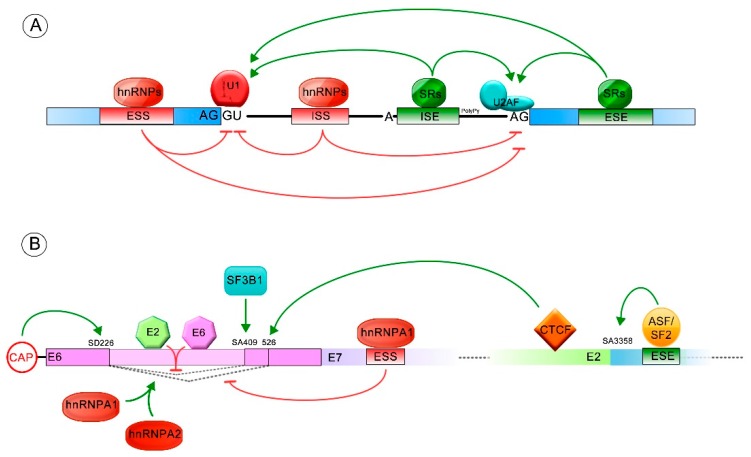
Figure 2.
Splicing regulation. Green arrows indicate positive splicing regulation, while red arrows represent negative splicing regulation. (A) General regulation mediated by cis and/or trans elements is shown. The exonic and intronic splicing enhancers (ESE and ISE) frequently stimulate the splicing process by binding to serine/arginine-rich proteins (SR proteins). The exonic and intronic splicing silencers (ESS and ISS) commonly repress the splicing process, through binding with heterogeneous ribonucleoproteins (hnRNP) regulatory proteins; (B) Splicing regulated by cis and trans acting elements, allowing formation of different E6/E6* transcript patterns. The ESS and ESE sequences (exonic splicing silencer and enhancer, respectively) and the splicing donor (SD) and acceptor (SA) sites involved in E6 splicing regulation are also shown.