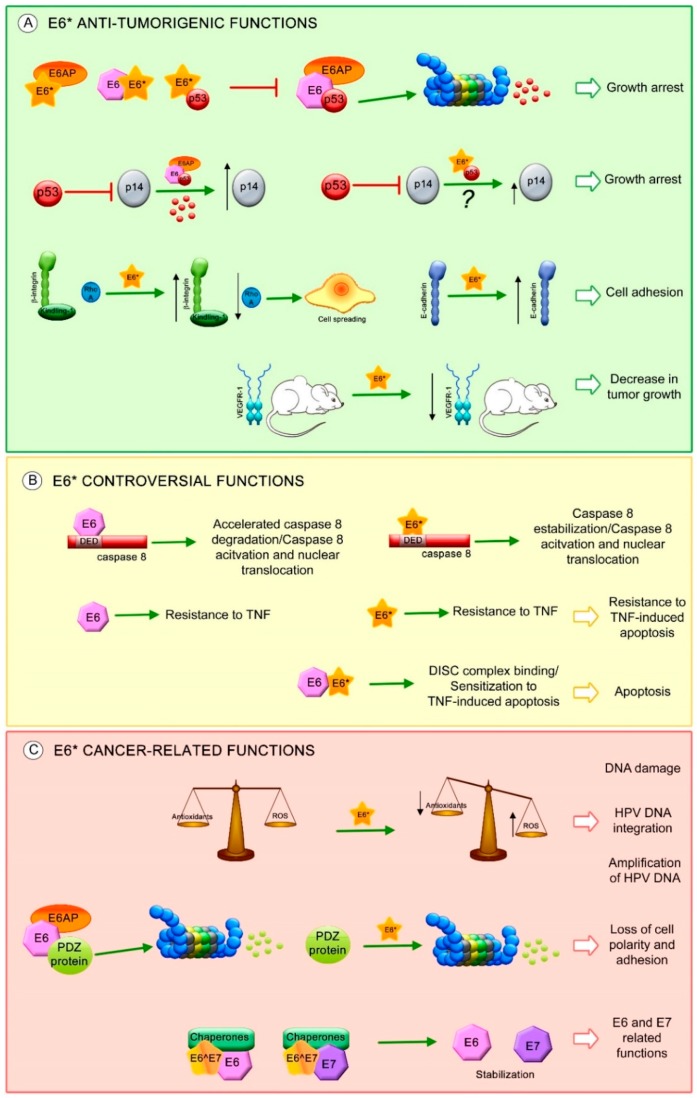
Figure 4.
E6* isoform-related functions. Proposed E6* functions involved in (A) anti-tumorigenic effects, such as: increase in growth arrest through inhibition of E6-mediated p53 degradation and increase in p14 protein levels possibly through E6*/p53 interaction (?), increase in cell adhesion by the activation of β-integrin signaling and overexpression of E-cadherin, decrease in tumor growth associated with a reduction in VEGFR-1; (B) Controversial effects of E6* in apoptosis regulation; and (C) Carcinogenic characteristics, such as: promotion of DNA damage by ROS, which may allow HPV DNA amplification and integration into the host genome, degradation of postsynaptic density-95/discs large/zonula occludens-1 domain (PDZ) containing proteins involved in cell polarity and adhesion and stabilization of E6 and E7 oncoproteins. The red T-bars indicate inhibition, the green arrows show induction of the related process, the black arrows depict an increment or a reduction in protein levels.