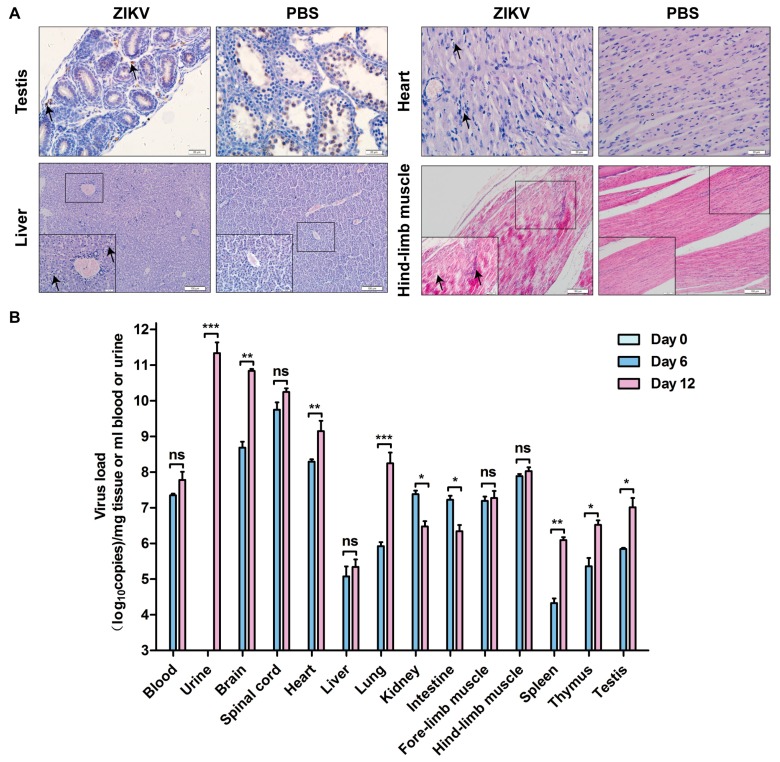
Figure 4.
ZIKV infects multiple organs of neonatal C57BL/6 mice. (A) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis of tissues after being infected with PRVABC59. The 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were infected i.p. with 106 TCID50 PRVABC59 per mouse or PBS. Mice were sacrificed at 11 dpi to isolate tissues for sectioning and being stained by IHC method. Representative pictures from PRVABC59-infected tissue slides were selected to show: testis, heart, liver, and hind-limb muscle; (B) Real time RT-PCR. The 1-day-old mice were infected i.p. with 106 TCID50 PRVABC59 per mouse for different days as indicated. The mice were then dissected following euthanasia at 0, 6, and 12 dpi to isolate the organs and tissues as indicated: blood, brain, spleen, heart, intestine, urine, heart, lung, fore-limb muscle, thymus, liver, kidney, hind-limb muscle, and testis. Total RNA samples were prepared using a GenMagSpin Viral DNA/RNA Kit (GenMag Bio, Beijing, China), and real-time RT-PCR was performed to determine the ZIKV RNA level in the isolated or collected organs and tissues. For each length of time kept, we used three mice. The average number of the RNA copies from the real time RT-PCR was obtained statistically with GraphPad Prism Software version 5.01. (the statistical significance was not determined. The graph only showed the average ± S.D.). Unpaired t test was used for statistical analysis. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns: not significant. Scale bars: A upper 20 μm, A lower 100 μm.