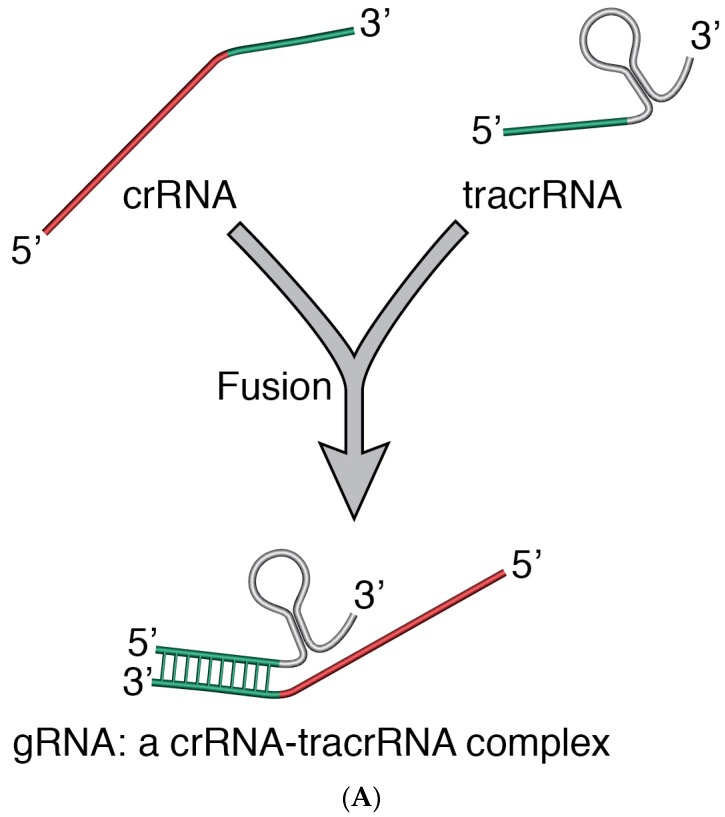
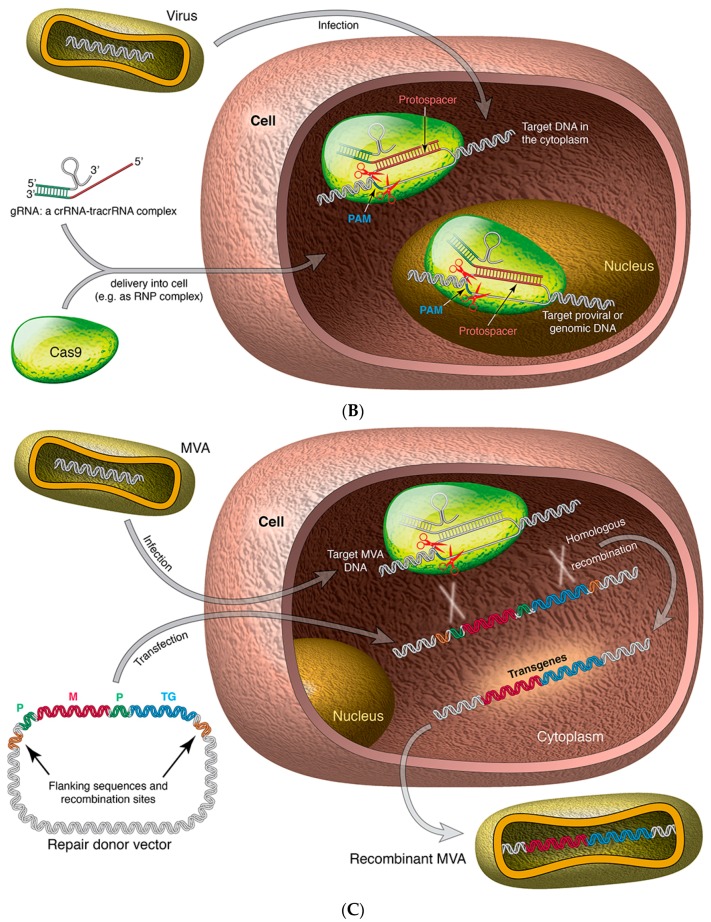
Figure 2.
(A) crRNA and tracrRNA are fused to form the sgRNA; (B) sgRNA interacts with Cas9 and with a section (a short homologous sequence of about 20 nt –protospacer) on the target DNA (e.g., a virus, provirus or genomic DNA), thus directing the Cas9 to a specific site on a target DNA. The Cas9 nuclease activity results in a double stranded cut (indicated with the scissors) in the target DNA; the cut stimulates the cell’s DNA repair mechanism. RNP Complex: Cas9/gRNA Ribonucleoprotein. (C) In the presence of a DNA template with flanking sequences homologous to the cut regions of a target DNA, the Homology Directed Repair (HDR) mechanism can be activated and be exploited to generate a recombinant virus, e.g., recombinant MVA. M: marker gene; TG: foreign gene; and P: promoter.