Figure 1.
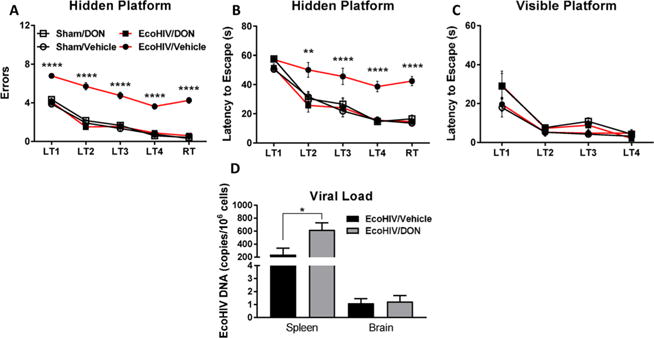
DON (14) prevented cognitive decline in the EcoHIV model of HAND. DON (14) treatment (1 mg/kg, ip) was begun prior to EcoHIV inoculation and continued every other day throughout the 30 day infection period and during radial arm water maze (RAWM) testing. 14 significantly attenuated spatial learning and memory deficits in the RAWM as measured by (A) number of errors across learning trials (LT) 1–4 and the retention trial (RT) and (B) latency to escape to a hidden platform relative to sham-inoculated control mice. 14 had no effect on (C) RAWM escape latency to a visible platform. 14 treatment also caused (D) a slight increase in EcoHIV viral load as measured by DNA copies in the spleen but had no effect on viral load in the brain. Behavioral comparison conducted by two-way ANOVA, posthoc comparison by Tukey’s test; ****p < 0.0001, EcoHIV/Veh vs Sham/Veh, EcoHIV/DON, and Sham/DON. Viral load comparison conducted by t test, *p < 0.05, n = 8/group.
