Figure 2.
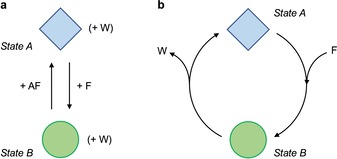
a) A mechanical molecular switch that uses a fuel (F) and an anti‐fuel (AF) to convert between two structurally different equilibrium states. Repeated switching (cycling) between the states requires the sequential addition of reactants. b) An autonomous chemically driven molecular machine that exploits the catalytic decomposition of a fuel to perform the transformation between two structurally different states. The process can continue indefinitely without the intervention of an operator as long as the fuel is available. Waste products (W) are formed in both cases.
