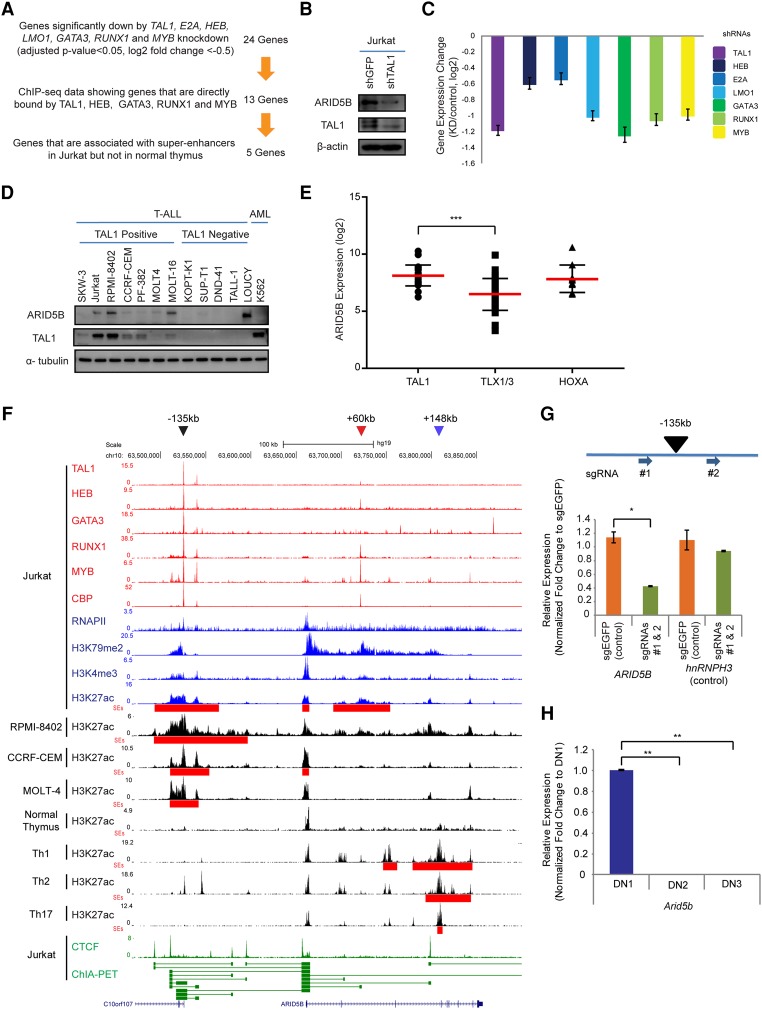
Figure 1.
The TAL1 complex positively regulates the ARID5B gene in T-ALL cells. (A) Filtering criteria for identifying genes directly activated by the TAL1 transcriptional complex and associated with the SE in the T-ALL cell line Jurkat. We first selected 24 genes that are commonly regulated by all seven transcription factors involved in the TAL1 complex. (B) Western blot analysis for protein expression of ARID5B, TAL1, and β-actin (loading control) in Jurkat cells on day 3 after shRNA-expressing lentivirus infection. (C) mRNA expression level of ARID5B after knockdown of TAL1, HEB, E2A, LMO1, GATA3, RUNX1, and MYB in Jurkat cells analyzed by RNA-seq. (D) Western blot analysis for protein expression of ARID5B, TAL1, and α-tubulin (loading control) in T-ALL and AML cell lines. (E) The mRNA expression level of ARID5B in primary T-ALL cases analyzed by microarray analysis using a publicly available data set (Homminga et al. 2011). T-ALL cases were classified into subgroups based on the expression of transcription factors (TAL1, TLX1/3, and HOXA). (***) P < 0.001 by two-sample two-tailed t-test. (F) ChIP-seq gene tracks showing the binding locations of the TAL1 complex (TAL1, HEB, GATA3, RUNX1, and MYB), the coactivator protein CBP, and RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) at the genomic region around the ARID5B gene in a T-ALL cell line (Jurkat). ChIP-seq data for H3K79me2 and H3K4me3 were used to represent transcription initiation and elongation, respectively. H3K27ac and SEs (red bars) for T-ALL cell lines (Jurkat, RPMI-8402, CCRF-CEM, and MOLT-4) and normal T cells (thymus; Th1, Th2, and Th17) are shown. The ChIP-seq profiles of CTCF and cohesin in Jurkat were analyzed using a chromatin–chromatin interaction analysis by paired-end tag sequencing (ChIA-PET) interaction data set reported by Hnisz et al. (2016). The horizontal green lines linking two bars illustrate a chromatin–chromatin interaction. Black, red, and blue arrowheads indicate SEs around the −135-kb, +60-kb, and +148-kb regions, respectively. (G) Single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs: #1 and #2) were designed to knock out the −135-kb element and deliver it by lentiviral infection into Jurkat cells. The mRNA expression of ARID5B and its neighboring gene, hnRNPH3 (control), in knockout cells was measured on day 6 after lentivirus infection by quantitative RT–PCR (qRT–PCR) analysis. The relative gene expression was normalized to GAPDH expression. (*) P < 0.05 by two-sample two-tailed t-test. (H) Expression of the mouse Arid5b gene in normal thymocytes at different stages: double-negative 1 (DN1; CD44+CD25−), DN2 (CD44+CD25+), and DN3 (CD44−CD25+). The mRNA expression of Arid5B was analyzed by qRT–PCR and normalized to β-actin expression. Fold change values compared with the expression in DN1 cells are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of duplicate samples. (**) P < 0.01 by two-sample two-tailed t-test.