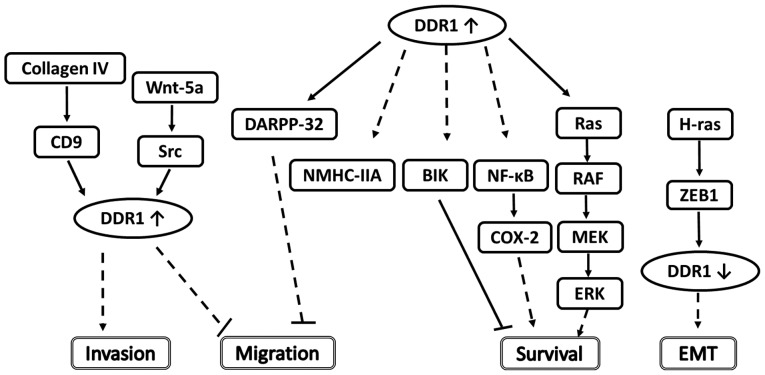
Figure 1.
Reported DDR1-associated signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. The mechanisms for the effect of ZEB1, COX-2, DARPP-32 and Wnt-5a on the migration, survival, EMT and invasion regulatory networks are illustrated. Solid lines indicate direct interactions or effects, whereas dashed lines indicate indirect interactions or effects through one or more intermediate steps. Pointed and flat arrows indicate activating and inhibiting effects, respectively. DDR1, discoidin domain receptor 1; ZEB1, zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; DARPP-32, dopamine- and cAMP-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; CD9, cluster of differentiation 9; NMHC-IIA, non-muscle myosin heavy chain-IIA; BIK, Bcl-interacting killer; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; MEK, ERK activator kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase.