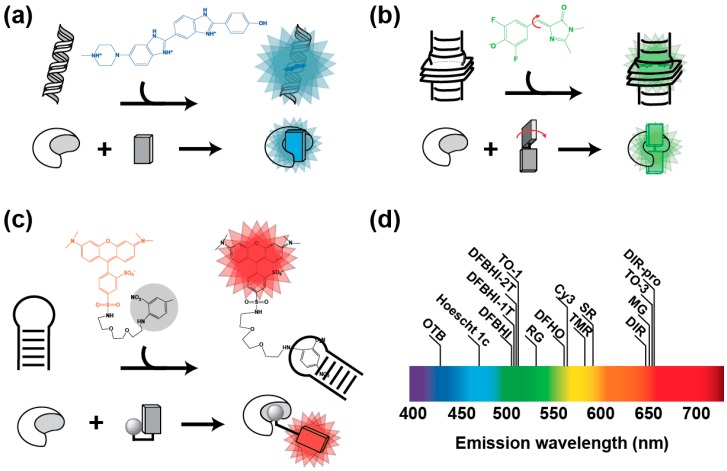
Figure 1.
Main conception strategies of fluorogens. (a) Environment sensitive fluorogens. Molecules such as Hoescht 33258 (formula in blue) emit blue fluorescence upon association with DNA minor groove. Modifying the fluorogen with bulky groups allows aborting this non-specific DNA binding capacity, while preserving the fluorogenic capacity that can be now specifically activated by the cognate aptamer [35]. (b) Molecular rotor fluorogens. DFHBI (formula in green) [29] eliminates excitation energy by molecular movements (red arrows). However, upon association to the cognate aptamer, movements are restricted and fluorogen energy is eliminated by fluorescence emission. (c) Quenched fluorogens. Sulforhodamine B (formula in red) fluorescence is quenched by a conjugated dinitroaniline (formula in black and shaded in gray) [32]. However, the fluorescence is restored upon the specific recognition of the quencher (or the fluorophore moiety in other systems) by an aptamer. In every example, RNA aptamer is represented by the croissant-shaped object and the fluorogen by the rectangles. (d) Distribution of fluorogen emission wavelength along the visible spectrum.