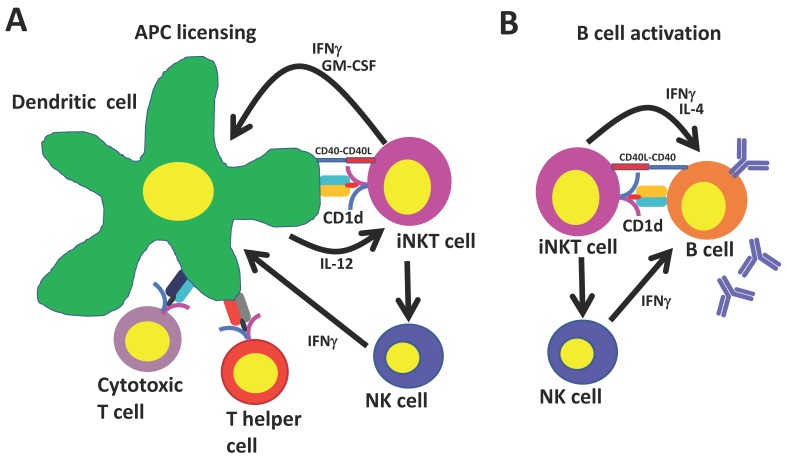
Figure 1.
Universal T helper cell functions of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells. (A) iNKT cells mature and license dendritic cells when they recognize agonist-bound CD1d. iNKT cells upregulate CD40L and secrete interferon gamma (IFNγ) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), which induces costimulatory molecule expression and the production of interleukin (IL)-12 by dendritic cells. This further stimulates iNKT cells and primes CD8+ T cells against copresented peptide epitopes. iNKT-conditioned dendritic cells promote conventional CD4+ T cell help to peptide antigens, which leads to additional enhancement of CD8+ T cell responses and promotes the generation of follicular T helper cells; (B) iNKT cells binding cognate antigen on CD1d-expressing B cells differentiate into iNKT follicular helper cells, which resemble conventional helper cells in their ability to augment B cell responses through a CD40–CD40L dependent mechanism. iNKT cells may also boost humoral immunity by transactivating NK cells that can stimulate B cells to secrete immunoglobulin G (IgG).