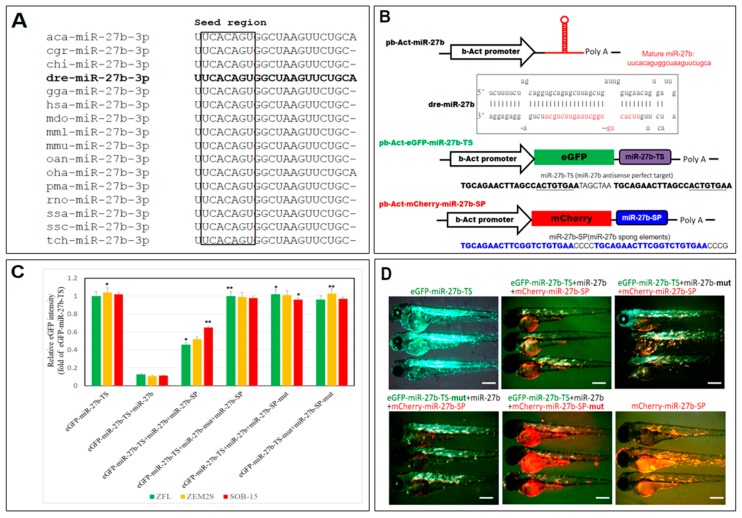
Figure 1.
Design and validation of a miR-27b-sponge (miR27b-SP). (A) Alignment of the mature miR-27b sequence is perfectly conserved across many species, including arboreal lizard (Anolis carolinensis; aca-miR-27b), chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus; cgr-miR-27b), domestic goat (Capra hircus; chi-miR-27b), zebrafish (Danio rerio; dre-miR-27b), red junglefowl (Gallus gallus; gga-miR-27b), humans (Homo sapiens; hsa-miR-27b), gray short-tailed opossum (Monodelphis domestica; mdo-miR-27b), rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta; mml-miR-27b), mouse (Mus musculus; mmu-miR-27b), platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus; oan-miR-27b), king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah; oha-miR-27b), sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus; pma-miR-27b), rat (Rattus norvegicus; rno-miR-27b), Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar; ssa-miR-27b), wild boar (Sus scrofa; ssc-miR-27b) and chinese tree shrew (Tupaia chinensis; tch-miR-27b). (B) Cloning of pri-miR-27b and miR27b-SP into b-Act expression vectors. Stem-loop structure of premiR-27b is shown, in which mature miR-27b is highlighted in red. (C) In vitro EGFP reporter assays were performed to confirm the direct interaction between miR-27b and the target sequences. ZFL, ZEM2S, and SOB-15 cells were transfected with indicated b-Act-miR-27b plasmids, and the EGFP intensity was measured. * p < 0.01, and ** p < 0.005. (D) In vivo EGFP reporter assays were performed to confirm the direct interaction between miR-27b and the target sequences in six days post fertilization (dpf) zebrafish larvae.