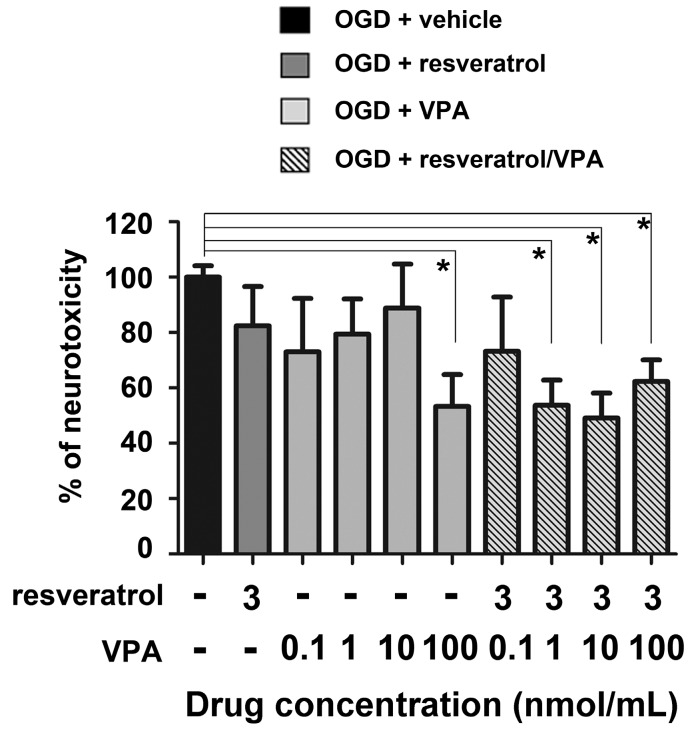
Figure 1.
Valproate (VPA) and resveratrol elicited neuroprotective effects in primary cortical neurons exposed to oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD). VPA (100 nmol/mL), added during the 24 h recovery period, showed per se a significant neuroprotective activity. The combination of concentrations, per se ineffective, of resveratrol (3 nmol/mL) and VPA (1 nmol/mL) led to maximal neuroprotection. Values were expressed as a percentage of neurotoxicity, measured performing an lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay. Bars depicted the mean ± s.e.m. (Standard Error of the Mean) from three separate experiments run in triplicate. * p < 0.05 versus the corresponding OGD value. For statistical analysis one way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test was performed.