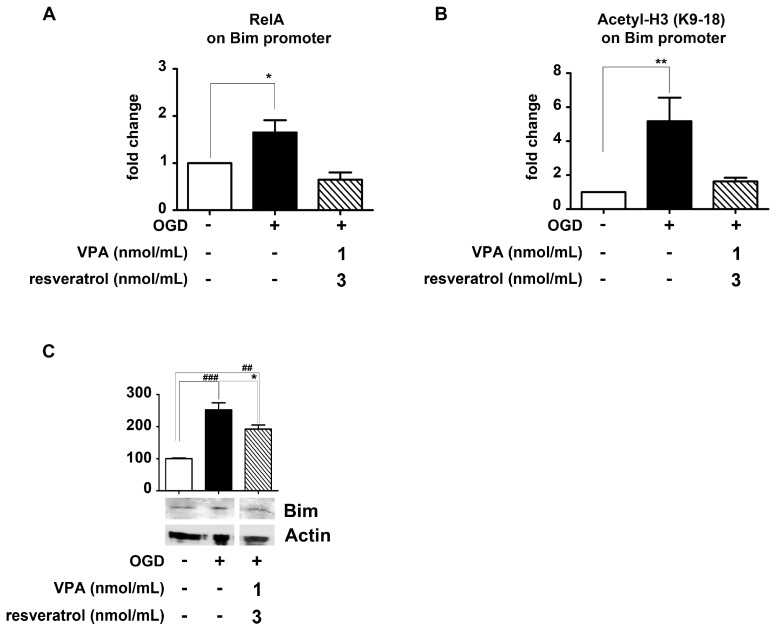
Figure 4.
Effect of valproate (VPA) and resveratrol combination on RelA detachment from Bim promoter and reduction of Bim protein level, in primary cortical neurons exposed to OGD. (A,B) Cortical neurons were exposed to OGD and then treated 2 h with a combination of VPA (1 nmol/mL) and resveratrol (3 nmol/mL). Treatment with the drug combination significantly reduced the RelA binding to, and the H3 acetylation (K9/18) at, the Bim promoter. Results were obtained by real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analyses of Bim promoter in immunoprecipitated DNA. Data were expressed as fold changes over values obtained in cells maintained in normal oxygen–glucose condition. Bars depicted the mean ± s.e.m. of three separate experiments, * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 versus the corresponding control value; (C) Treatment with combined VPA (1 nmol/mL) and resveratrol (3 nmol/mL) significantly attenuated the Bim protein increase after OGD exposure. In the densitometry analysis of immunoblot bands data were expressed as a percentage of the corresponding control value. Bars depict the mean ± s.e.m. of three separate experiments, ## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001 versus the corresponding control value; * p < 0.05 versus the corresponding OGD value.