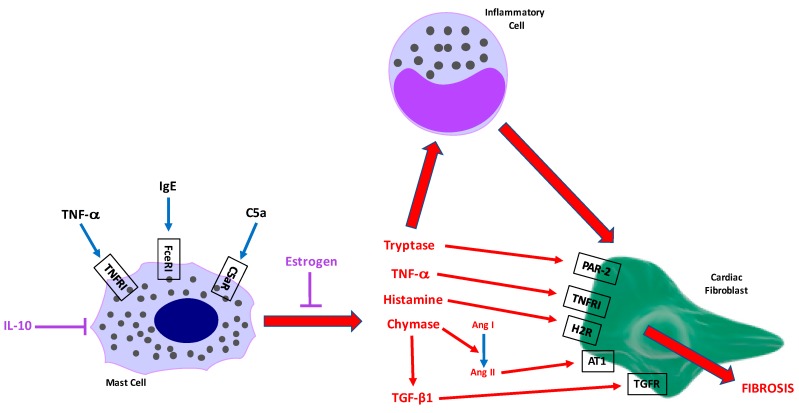
Figure 2.
Schematic depicting potential MC activation stimuli and interactions with other cell types that lead to cardiac fibrosis. Candidates for cardiac MC activation include IgE, TNF-α, and C5a. These then cause the release of MC mediators including the proteases tryptase and chymase, TNF-α, histamine, and TGF-β1. These mediators can then have direct effects on cardiac fibroblasts, but may also contribute to an inflammatory response that then activates cardiac fibroblasts via numerous cytokines. IL-10 and estrogen likely oppose cardiac MC activation/degranulation.