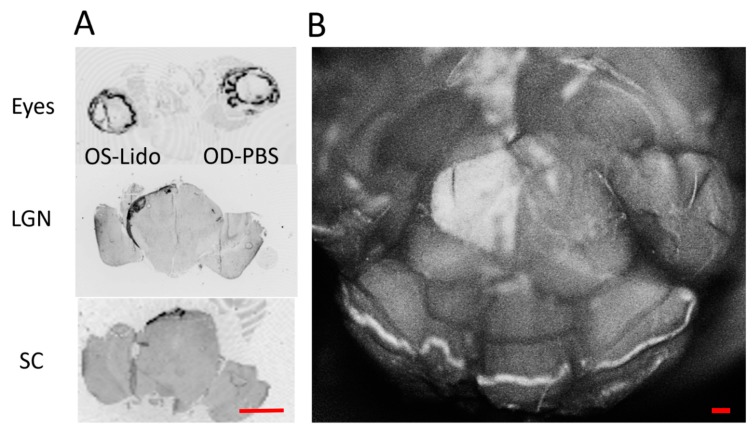
Figure 1.
Retrobulbar lidocaine blocks axon transport. (A) Representative consecutive tissue sections from the eyes to the brain one day after retrobulbar lidocaine in the left eye, immediately followed by intravitreal injection of Alexa Fluor 488 Cholera Toxin B in both eyes. Fluorescence is evident in both eyes but it is absent in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and Superior Colliculi (SC) contralateral to the left eye. Fluorescence is present in the LGN and SC contralateral to the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-injected right eye; scale bar, 200 µm. (B) Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy of the midbrain surface. The entire surface of the right SC receiving afferents from the lidocaine- injected right eye does not fluoresce, indicating impairment of axon transport in the lidocaine-treated eye; scale bar, 200 µm.