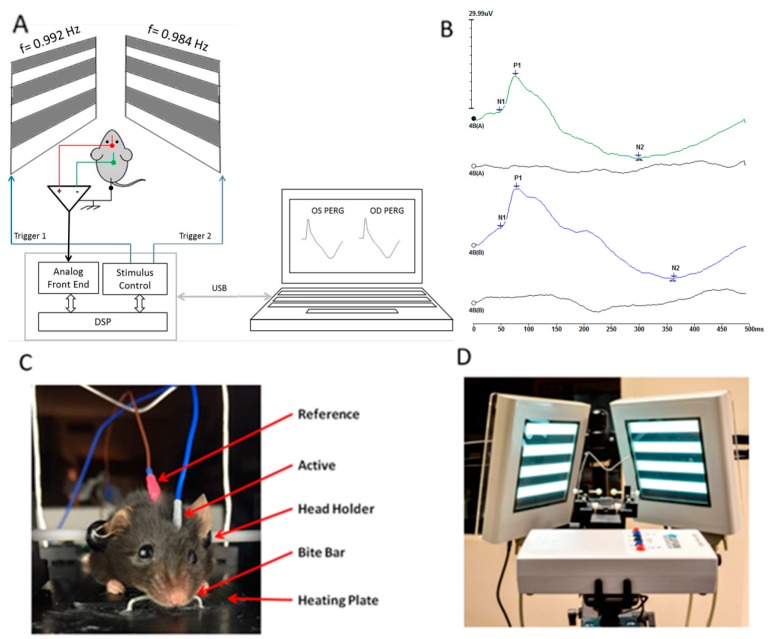
Figure 6.
(A) Mouse PERG recording layout; (B) PERG waveforms simultaneously recorded from each eye using one common electrode in the snout; (C) Mouse with non-corneal subcutaneous needle electrodes resting on a feedback-controlled thermostatic plate; (D) Patterned visual stimuli generated on high luminance (800 cd/sqm) LED displays and presented at each eye independently with slightly different reversal frequency (right eye: 0.984 Hz; left eye: 0.992 Hz). Asynchronous averaging allows isolation of monocular PERGs.