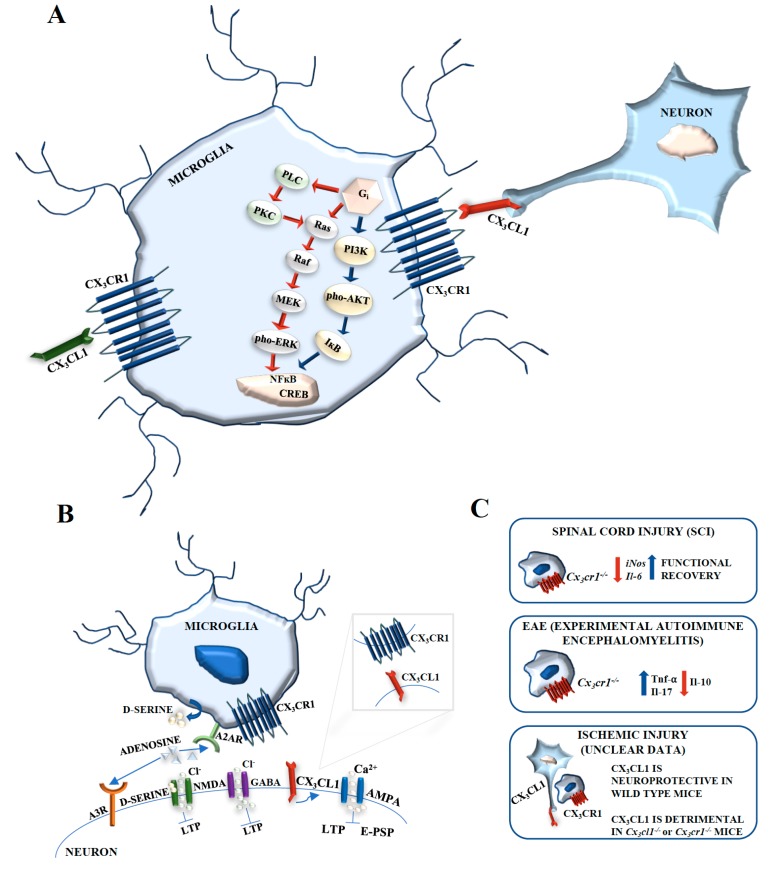
Figure 4.
CX3CL1-CX3CR1 signaling. (A) CX3CL1 induces transient phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. Soluble CX3CL1 activates the transcription factor CREB and ERK1/2 and induces the translocation of NF-κB p65 subunit to the nucleus. NF-κB p65 subunit nuclear translocation is avoided by a specific inhibitor of PI3-K, suggesting that CX3CL1-CX3CR1 activates NF-κB through Akt. (B) CX3CL1, acting through CX3CR1, modulates α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-metyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPA) phosphorylation leading to increased calcium entry and inhibition of both excitatory postsynaptic potentials and long-term potentiation. CX3CL1 can increase inhibitory postsynaptic currents, possibly by enhancing neuronal responsiveness to GABA-mediated chloride entry. CX3CL1 may activate CX3CR1 on microglia with consequent adenosine release that, in turn, could activate A3R receptors on neurons. Adenosine activates A2AR on microglial cells and induces the release of d-serine. The adenosine released by microglia has also been involved in neuroprotection by activating A1R receptor subtypes in neurons. (C) CX3CL1-CX3CR1 involvement in spinal cord injury, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and ischemic injury.