Figure 4.
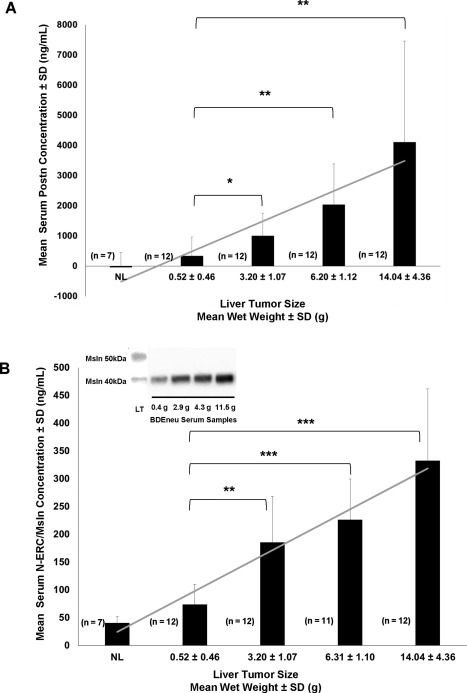
Serum Postn and Msln levels significantly increase as a function of progressive intrahepatic BDEneu cholangiocarcinoma growth. Serum Postn and Msln levels were determined by duplicate ELISA measurements made on separate serum samples prepared from exsanguinated blood obtained by cardiac puncture from individual rats. These were matched with corresponding liver tumors of different sizes obtained at the same time from the euthanized animals. Bar and linear graphs for (A) Postn and (B) Msln reflect a strong positive correlation between increased liver tumor weight and progressively elevated levels of each serum protein (Postn, r = 0.998, P ≤ 0.0001; Msln, r = 0.958, P ≤ 0.01). Postn was not detected by ELISA in serum samples from normal rats, but normal rat serum gave a very low Msln background value. Each bar represents the mean ± SD. *P ≤ 1 × 10−2, **P ≤ 3 × 10−4, ***P ≤ 1 × 10−6; n, number of animals analyzed per group. Inset in B illustrates protein bands of low to higher banding intensities for the ∼40‐kDa molecular weight form of Msln detected by western blotting of selected whole serum samples diluted 1:10 from rats with BDEneu liver tumors of various sizes from the same animal groups used for the ELISA measurements. LT represents a loaded control sample showing both the 50‐kDa and 40‐kDa Msln bands detected by western blotting within a whole protein lysate prepared from a 7.5‐g BDEneu liver tumor from the same experiment. Protein/well = 20 µg; g is the liver tumor sample wet weight in grams. Abbreviation: LT, liver tumor.
