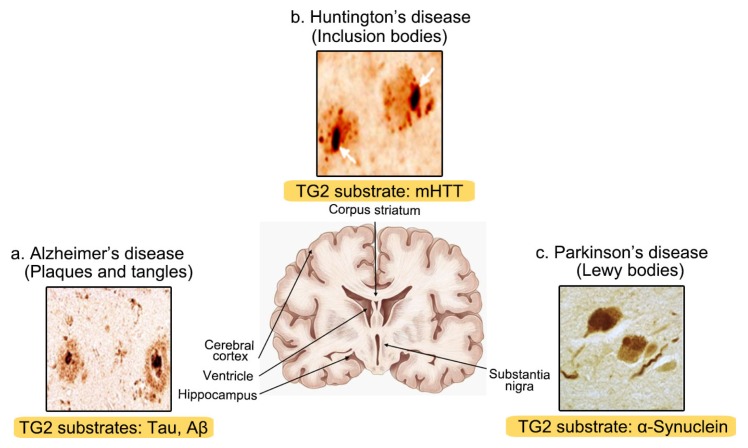
Fig. 2.
Characteristic features of insoluble amyloids consisting of intrinsically misfolded proteins, their specific CNS locations, and TG2-specific substrates in neurodegenerative diseases. (a) AD patients display the loss of neurons in the cerebral cortex, ventricle, and hippocampus. Extracellular amyloid plaques and intracytoplasmic neurofibrillary tangles with amyloid-β and tau, respectively, are the two main features of AD. (b) HD patients typically show the degeneration and atrophy of the corpus striatum. Intracellular inclusions primarily located in the striatum are mostly composed of mutant huntingtin. (c) PD patients have the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) of midbrain. Lewy bodies consisting mainly of α-synuclein are observed in PD. TG2 substrates are denoted in the brown-colored areas at the bottom of each NDD-characteristic inclusion, respectively (i.e. AD, plaques and tangles; PD, Lewy bodies; HD, mHtt).