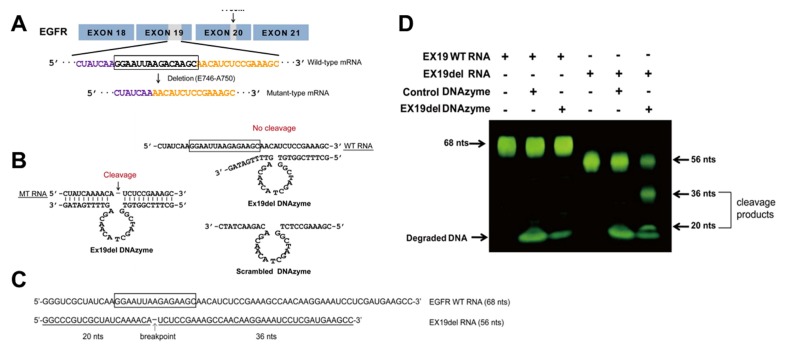
Fig. 1.
DNAzyme targeting mutant EGFR mRNA cleaves mutant RNA. (A) Sequence of mutant EGFR with a 15 nt-deletion in exon 19 (deletion from E746 to A750 in exon 19). (B) Sequences of Ex19del Dz (left) and scrambled DNAzyme (sc Dz, right). The DNAzyme-substrate mutant RNA (MT RNA) annealed complex is also shown. Ex19del DNAzyme was designed for cleavage of deletion type mRNA at a phosphodiester bond located between an unpaired adenine (A) and uracil (U). The site of cleavage by the DNAzyme is indicated by an arrow. (C) Sequences of each EGFR wild-type and deletion-type substrate RNA used for the cleavage reaction. (D) Exon 19 wild-type and mutant RNA substrates were incubated with Ex19del Dz and control DNAzyme (sc Dz) at 37°C for 3 h. The RNA products were analyzed by denaturing 10% PAGE (w/v) and visualized with SYBR Gold. DNAzyme was degraded with DNase to stop the reaction.