Fig. 4. Mll4 deletion impairs the exit of naive pluripotency.
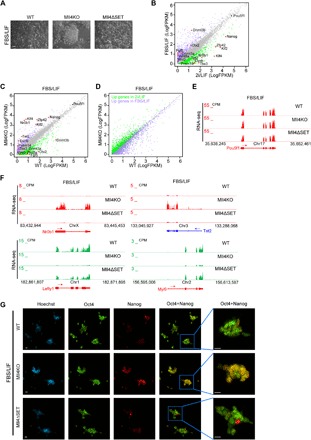
(A) Phase images of WT, Mll4KO, and Mll4ΔSET ESCs grown in FBS/LIF condition. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Correlation analysis of gene expression levels between ESCs grown in FBS/LIF and 2i/LIF conditions. Genes significantly up-regulated in FBS/LIF are labeled purple, whereas genes significantly increased in 2i/LIF are labeled green. The major naive pluripotency and primed pluripotency markers are marked, with red dots denoting significantly differentially expressed ones. (C) Correlation analysis of gene expression levels between WT and Mll4KO ESCs grown in FBS/LIF condition. Genes significantly down-regulated in Mll4KO cells are labeled green, whereas up-regulated ones are labeled purple. The major naive pluripotency and primed pluripotency markers are marked, with red dots denoting significantly changed ones. (D) Correlation analysis of the expression levels of DEGs in (B) between WT and Mll4KO ESCs grown in FBS/LIF condition. Genes significantly up-regulated in FBS/LIF are labeled purple, whereas genes significantly increased in 2i/LIF are labeled green. (E) UCSC genome browser view of RNA-seq signals of WT, Mll4KO, and Mll4ΔSET ESCs cultured in FBS/LIF condition at the Pou5f1 gene. (F) UCSC genome browser view of RNA-seq signals of WT, Mll4KO, and Mll4ΔSET ESCs cultured in FBS/LIF condition at Nr0b1, Tet2, Lefty1, and Myl9 genes. (G) Immunostaining of pluripotency factors Oct4 and Nanog in WT, Mll4KO, and Mll4ΔSET ESCs cultured in FBS/LIF condition. Scale bars, 10 μm.
