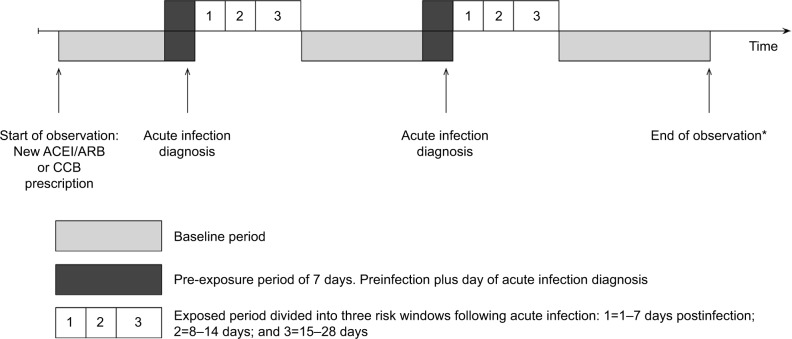
Figure 1.
Graphical representation of self-controlled case series study design.
Notes: Figure illustrates a single individual with an acute infection (UTI, LRTI, or gastroenteritis) during their observation period. All participants included in the analyses had at least one acute infection and at least one episode of AKI requiring hospital admission (analyses used first episode of AKI as the outcome and ignored subsequent AKI records). Rate ratios presented are pooled estimates derived from the rate of AKI events during risk (exposed) periods divided by the rate of events during baseline periods; age is adjusted for at all stages of analysis. Incident AKI can occur during any one of six exposure periods: baseline, 7 days prior to infection, day of infection, 1–7 days postinfection, 8–14 days postinfection, or 15–28 days postinfection. *Follow-up ends at the earliest of death, the end of registration, last collection date from GP, or 30/60/90 days after the end of first break in ACEI/ARB or CCB treatment of 30/60/90 days or more.
Abbreviations: ACEI/ARB, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker; AKI, acute kidney injury; CCB, calcium channel blocker; GP, general practitioner; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection; UTI, urinary tract infection.