Fig. 5.
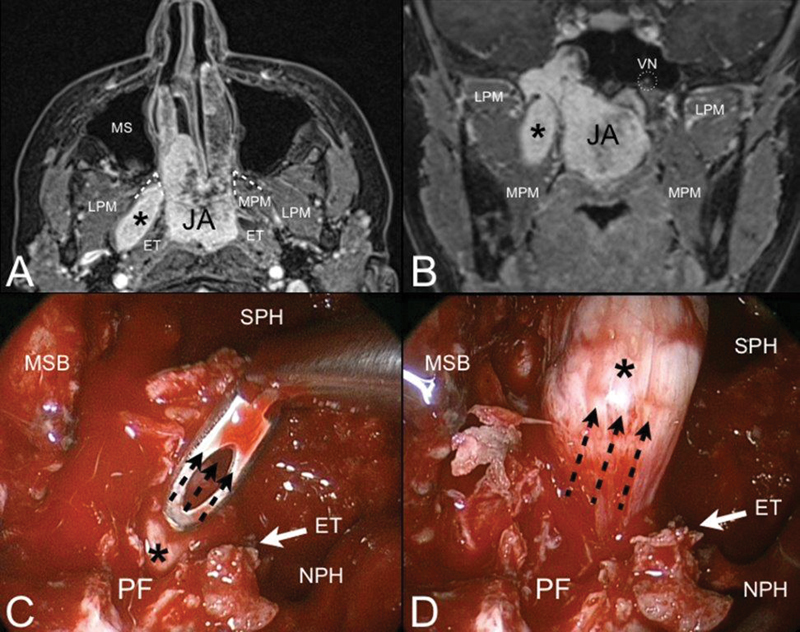
Axial ( A ) and coronal ( B ) contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR). Juvenile angiofibroma (JA) with finger-like retropterygoid extension (black asterisk). Through the bone of the pterygoid root, JA extents to the pterygoid fossa (PF) and follows the direction of the medial pterygoid muscle (MPM) staying behind the auditory tube (ET). Endoscopic view of the right nasal fossa during the endoscopic procedure ( C, D ). The transpterygoid approach allows to expose the pterygoid fossa and pull up (black dashed arrows) the retropterygoid extension of the lesion. Abbreviations: LPM, lateral pterygoid muscle; MS, maxillary sinus; MSB, middle skull base; NPH, nasopharynx; SPH, sphenoid sinus; VN, vidian nerve.
