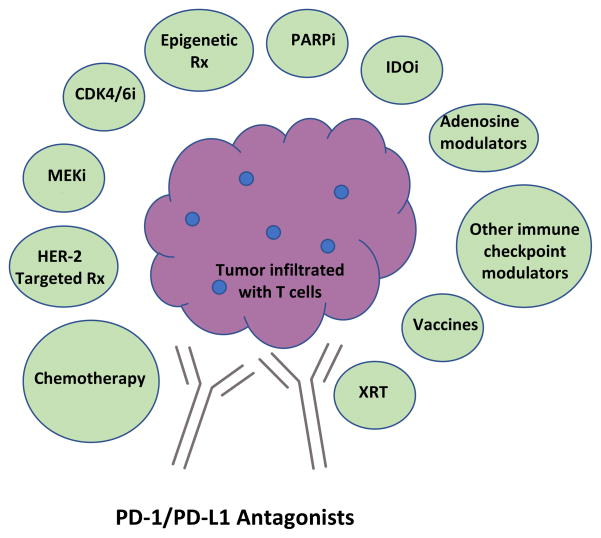
Figure 3. Summary of selected immunotherapy combinations for breast cancer treatment with strong mechanistic rationale.
Because blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has clear activity in multiple cancer, many regard it as a fundamental component of future cancer immunotherapies. Current clinical efforts are focused on developing immunotherapy combinations, many based on PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, that convert nonresponders to responders, deepen responses that do occur, and surmount acquired immunotherapy resistance. Other combinations, some of which include PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, are also in development. Abbreviations: PD-1=programmed death receptor-1; PD-L1=programmed death ligand-1; chemo=chemotherapy; HER-2=human epidermal growth factor receptor-2; Rx=therapy; MEKi=mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK) inhibitor; CDK4/6i=cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor; PARPi=poly (adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose polymerase inhibitor; IDOi=indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase inhibitor, XRT=radiotherapy.