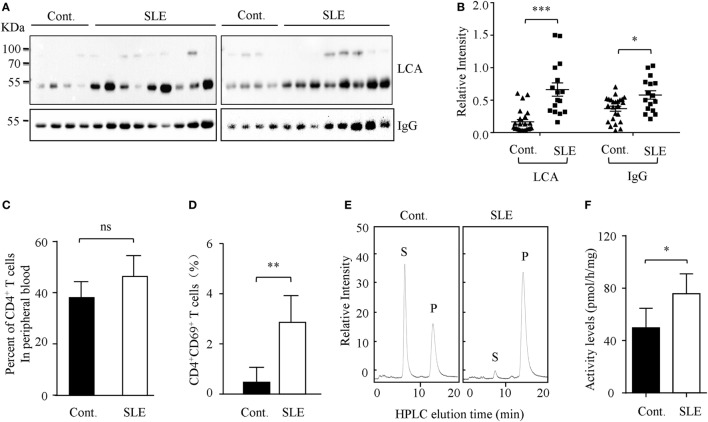
Figure 1.
Core fucosylation was significantly increased in the systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. (A) The sera of SLE patients were analyzed by lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA) blot and Western blot. Plates were incubated with biotin-conjugated LCA (1:20,000). Comparable results were obtained in three independent experiments. (B) Densitometric analysis of the bands of IgG and LCA in sera in SLE patients. Data are shown as mean values ± SEM (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001). (C) The percentage of CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood of SLE patients. (D) The percentage of CD4+CD69+ T cells in the peripheral blood of SLE patients (n = 17). (E,F) FUT8 activities in the CD4+ T cells of SLE patients by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). CD4+ T cells were isolated with anti-CD4 Ab-conjugated magnetic beads. The sorted cell populations were routinely more than 96% pure. Five micrograms cell lysates as the enzyme source were mixed with the assay buffer. After incubation at 37°C for 8 h, 10 µL of the supernatant was subjected to HPLC. Activity was expressed as pmol of GDP-fucose transferred to the acceptor per hour per milligram of protein. Data are shown as mean values ± SD (n = 17; ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). S is the peptide substrate and P is the product of fucosylation.