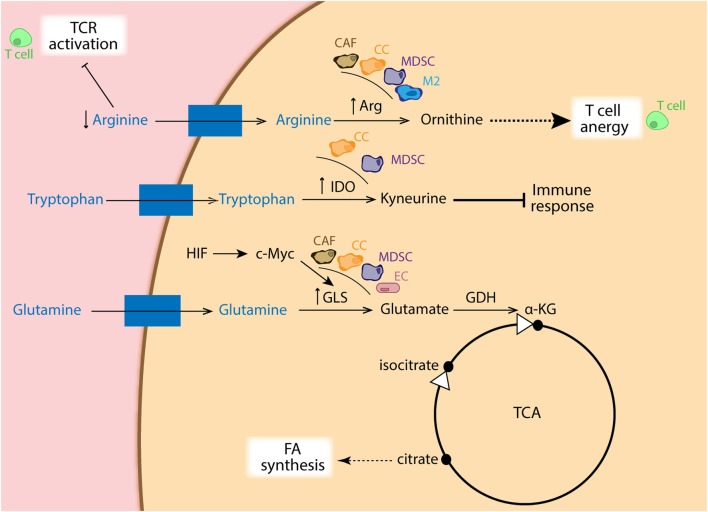
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of amino acid metabolism in different cell types. Cancer cells (CCs: orange), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs: brown), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs: purple), as well as M2 macrophages (blue) show increased expression of arginase, depleting the surrounding environment of arginine, which is essential for TCR activation in T cells (green). Ornithine coming from arginase metabolism also dampens T cell activation. Moreover, increased expression of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in CC and MDSCs favors catabolism of tryptophan into kyneurine, with immune suppressive effects. In addition, overexpression of GLS via HIF/c-Myc regulation in CA, CAFs, MDSCs, and endothelial cells (ECs: pink) generates glutamate, which is used to replenish intermediates of the TCA cycle, favoring FA synthesis from citrate.