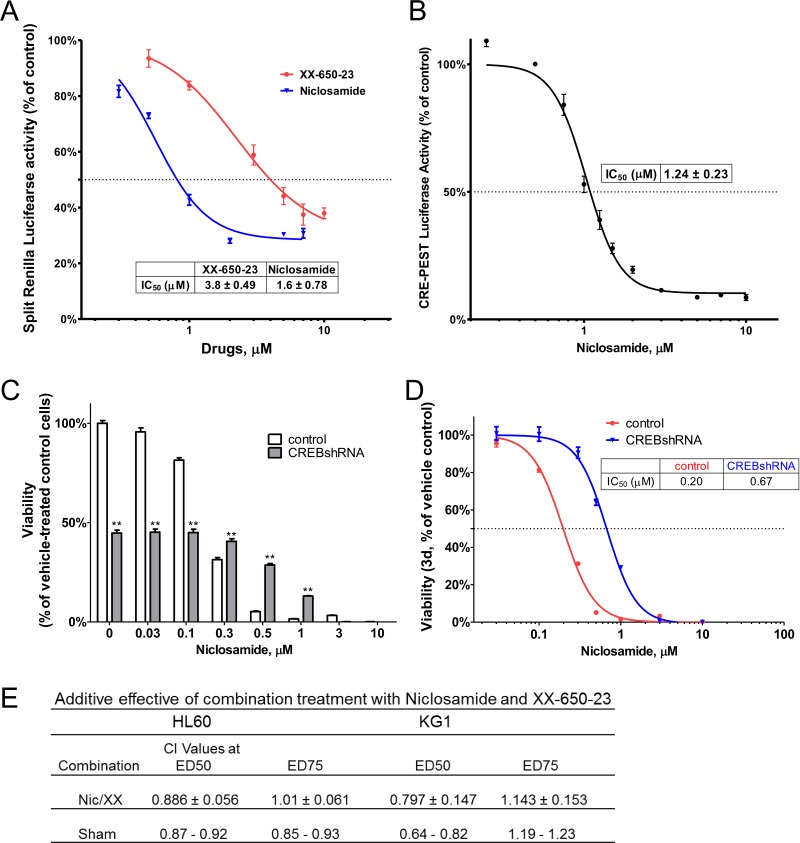
Figure 2. Niclosamide inhibits CREB-dependent pathways.
A. Niclosamide was more potent than XX-650-23 to inhibit CBP KIX-CREB KID domain interaction. RLucC-KIX and KID-RLucN expressing vectors were transfected into 293 cells. Transfected 293 cells were treated with compounds 30 minutes before forskoin (6 μM) stimulation. Cells were further incubated for 90 minutes, and measured Renilla luciferase activity using coelenterazine afterwards. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). B. HL60 cells expressing CREB-driven luciferase were generated. Cells were treated with niclosamide for 6h. Luciferase activity was significantly inhibited by niclosamide treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). The IC50s are described in the graphs. C. CREB knockdown AML cells were more resistant to niclosamide. HL60 cells were transduced with CREB or control shRNA lentivirus. Transduced cells were treated with niclosamide for 3 days. Cell Titer Glo assays were performed. The graph shows that CREB knockdown itself inhibited cellular viability of HL60 cells. Values are indicated as mean ± SEM (n = 3). **, p < .01. D. Viability dose-response curve for CREB shRNA transduced cells shifted to the right, suggesting more resistant cells. E. Additive effect of combination treatment with niclosamide and XX-650-23 in HL60 and KG1 cells. Cells were treated with various concentrations of niclosamide (Nic) and XX-650-23 (XX) for 3d. Viability was accessed using CellTiter-Glo assay kit. Combination index (CI) values were calculated by Chou-Talalay method using CalcuSyn software. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 4). Additivity ranges of CI scores were determined from sham mixtures of the same compound (niclosamide or XX-650-23) in each cell line.