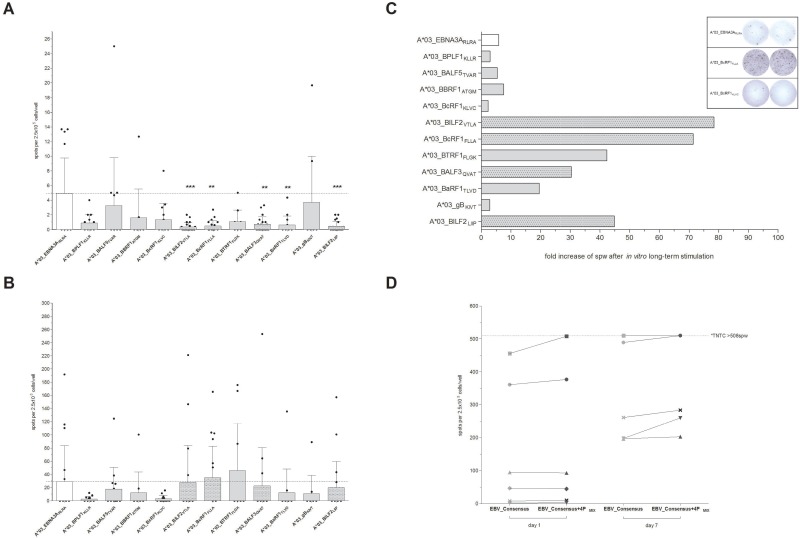
Figure 1.
(A–D) Screening for HLA-A*03:01-restricted EBV-peptide-specific T cells by IFN-γ EliSpot. EBV-specific T-cell responses elicited by EBV-derived candidate-peptides were determined by IFN-γ EliSpot assays using PBMCs from healthy HLA-A*03:01-positive and EBV-seropositive donors (n ≥ 10). The known immunodominant HLA-A*03:01-specific T-cell epitope A*03_EBNA3ARLRA and the available PepTivator EBV Consensus (EBV_Consensus) served as references. Results are indicated as the number of spots per well (spw) after the number of spw of the respective negative control has been subtracted from that one of the antigen well. Based on the cut-off value of >3 peptide-induced spw, donors were identified as positive responders. EBV-peptides initiating an immune response in >50% of the donors after seven days of in vitro stimulation were classified as highly immunodominant. IFN-γ EliSpot assays after (A) short-term (day 1) and (B) long-term (day 7) in vitro stimulation with one of the peptides. (C) The capacity of the EBV-peptides to generate EBV-specific T cells subsequent to long-term in vitro stimulation is separately demonstrated for each of the peptides by the resultant fold increases of spw. (D) The immunogenic potential of the respective peptides to reinforce available peptide pools (e.g. EBV_Consensus) was evaluated by means of comparing the resultant spw ensuing stimulation (‘day 1’ and ‘day 7’) with EBV_Consensus+4PMIX (Table 1) to the respective values of the mere EBV_Consensus. Numbers of spw, too high to be individually detected by the EliSpot reader (>508 spw based on the highest determined count of spw), are indicated by the broken line. Results are displayed as individual results and means ± standard deviation (SD). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the EBV-specific peptides and A*03_EBNA3ARLRA (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).