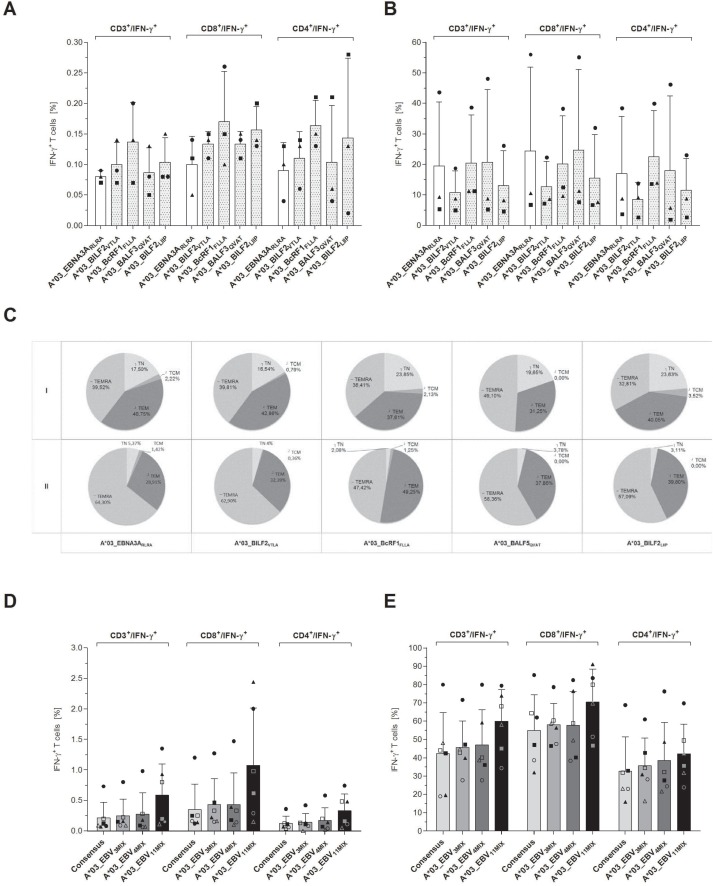
Figure 6.
(A–E) Evaluation of the eligibility of the highly immunodominant HLA-A*03-restricted EBV-derived peptides for clinical application–by means of CSA. PBMCs from healthy donors (n = 3) were stimulated with one of the four highly immunodominant EBV-peptides. Respective frequencies of the IFN-γ-secreting cell fractions before (origin) and after the enrichment (eluate) were determined by multicolor flow cytometry. Frequencies in the ‘origin’ evaluated in comparison to (A) the respective frequencies of the IFN-γ-secreting T cells in response to the EBV-derived reference peptide A*03_EBNA3ARLRA. (B) The efficiency of the IFN-γ-specific enrichment via the magnetic labeling of IFN-γ-secreting cells is separately shown for each of the assessed peptides. (C) Phenotypic analyses regarding naïve (TN), central memory (TCM), effector memory (TEM) and terminally differentiated effector memory (TEMRA) T cells were performed for the IFN-γ+CD8+-secreting T cells of both aliquots (I: Origin, II: Eluate) and are visualized by the respective mean frequencies. To determine the peptides’ aptitude to enhance the stimulating efficacy of the EBV_Consensus, three mixtures of the in vivo isolated peptides and the EBV_Consensus were used as stimulating antigens (EBV_Consensus+3PMIX, EBV_Consensus+4PMIX, EBV_Consensus+11PMIX, Table 1). The frequencies of the different cell fractions in the ‘origin’ (n = 6) are individually displayed (donor 1 = ●, donor 2 = ■, donor 3 = ▲, donor 4 = ○, donor 5 = □ donor 6 = Δ) in comparison to the respective percent values of the (D) IFN-γ+CD3+-secreting T cells, IFN-γ+CD8+-secreting T cells and IFN-γ+CD4+-secreting T cells, respectively, induced by the mere EBV_Consensus. The efficiency of the enrichment is furthermore individually shown for each of the donors (n = 6) using the percent values of (E) the IFN-γ+CD3+-secreting T cells, the IFN-γ+CD8+-secreting T cells and the IFN-γ+CD4+-secreting T cells. Findings are displayed as individual results and as the mean percentage of IFN-γ+ T cells ± SD.